You play a critical role in maintaining safety on every jobsite. Eye bolt testing helps you prevent failures that could cause injury or equipment loss. When you use certified eye bolts from Powerful Machinery, you trust components built for strength and reliability. Industry data highlights the difference:
Feature | Certified Eye Bolts | Non-Certified Eye Bolts |
|---|---|---|
Manufacturing | Hot-forged, single-piece construction | Bent or welded steel wire |
Strength | Superior fatigue resistance | Poor mechanical properties |
Application | Rated for lifting and rigging | Light-duty, non-load-bearing uses |
Failure Mode | Predictable at ultimate load | Sudden, unpredictable failure |
Safety | Required for safety-critical work | Not for worker or product safety |
Regular inspection and adherence to international standards keep your projects secure and compliant.
Key Takeaways
Regularly inspect eye bolts to ensure safety and compliance. Schedule inspections based on usage frequency.
Conduct visual inspections for cracks, corrosion, and thread damage before each use. Remove any defective eye bolts immediately.
Use a pull-out tester to verify the tensile load capacity of eye bolts. Ensure loads are applied correctly to prevent failures.
Utilize go gauges to confirm the dimensional accuracy of eye bolts. This ensures only compliant parts pass inspection.
Choose certified eye bolts from trusted manufacturers like Powerful Machinery to enhance safety and reliability on the jobsite.
Eye Bolt Testing Methods
You must use reliable eye bolt testing methods to ensure safety and compliance on every project. Powerful Machinery’s certified stainless steel eye bolts meet international standards, making them ideal for construction, marine, and industrial environments.
Regular testing helps you detect wear, deformation, or improper installation before failure occurs.
Tip: Schedule inspections based on usage frequency and workplace demands.
Inspect equipment at key points throughout its service life.
For heavy use, conduct quarterly or monthly inspections.
For less frequent use, annual inspections may suffice.
Assign a competent person to perform each inspection.
Visual Inspection of Eyebolts

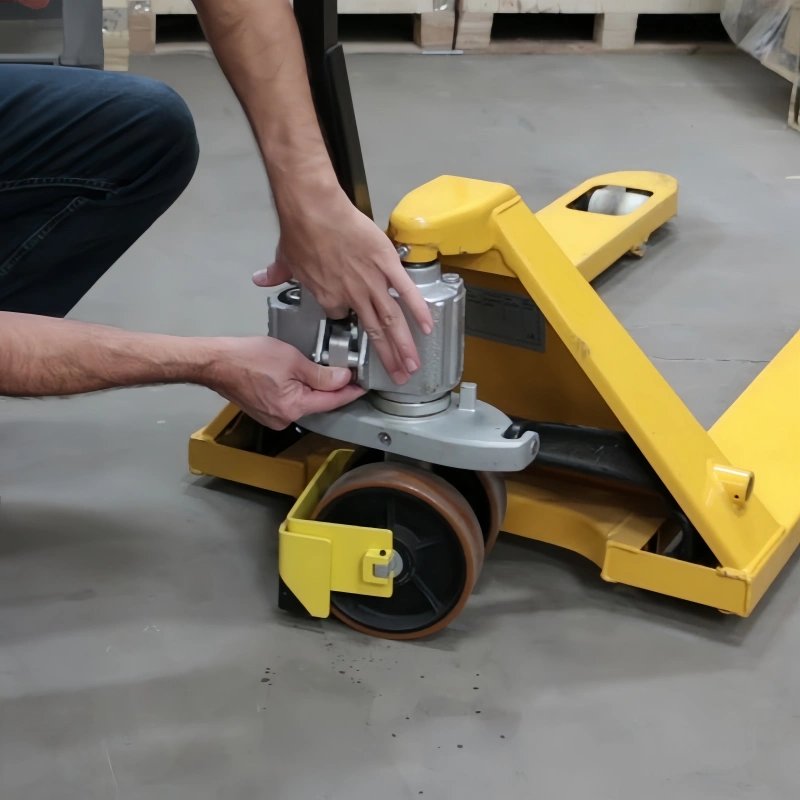
Begin each eye bolt testing session with a thorough visual inspection. Look for cracks, corrosion, thread damage, or signs of deformation. Check that the eyebolt sits flush and that the threads engage fully. If you find any defects, remove the component from service immediately.
This step is essential for preventing accidents and maintaining compliance.
Pull-Out Force Test for Eyebolts
Use a pull-out tester to verify the tensile load capacity of each eye bolt. This test measures the force required to pull the bolt from its anchor point. Compare your results to the minimum requirements for your application. The table below shows typical minimum pull-out forces for different diameters:
Diameter | Straight Pull (lbs) | 45° Pull (Shoulder Only) (lbs) |
|---|---|---|
1/4″ | 500 | 125 |
5/16″ | 900 | 225 |
3/8″ | 1,300 | 325 |
7/16″ | 1,800 | 450 |
1/2″ | 2,400 | 600 |
9/16″ | 3,000 | 800 |
5/8″ | 4,000 | 1,000 |
3/4″ | 5,000 | 1,250 |
7/8″ | 7,000 | 1,750 |
1″ | 9,000 | 2,250 |
1-1/8″ | 12,000 | 3,000 |
1-1/4″ | 15,000 | 3,750 |
1-1/2″ | 21,000 | 5,250 |
1-3/4″ | 28,000 | 7,000 |
2″ | 38,000 | 9,500 |
2-1/2″ | 56,000 | 14,000 |
Always apply loads in the plane of the eye. Never exceed a 45-degree angle. Exceeding the rated load can cause failure and serious safety risks.
GO-NO-GO Gauge Testing
You must use appropriate go fixed gauges to confirm the dimensional accuracy of each eye bolt. Go-no go fixed gauges include a “Go” gauge, which checks if the part meets the maximum material condition, and a “No-Go” gauge, which ensures the part does not exceed the minimum material condition.
This method aligns with standards such as ASME Y14.5. When you use fixed gauges, you guarantee that only compliant parts pass inspection. Defective parts will fail, which helps you maintain safety and quality on every job.
Go-no go fixed gauges are essential for construction, marine, and industrial applications. You should always use fixed gauges during eye bolt testing to ensure compliance with international standards.
How to Test Eye Bolts Safely?

Preparation and Safety Checks
You must prepare thoroughly before you test eye bolts. Begin by gathering the right tools and safety equipment. Use a drill, correct drill bit size, wrench, hammer, safety glasses, gloves, dust mask, level, and measuring tape. These items help you work efficiently and protect yourself from hazards.
Inspect each lifting eye bolt for heavy wear, corrosion, or thread damage. Look for heat damage, weld spatter, or arc strikes. Never use eye bolts that have been altered or repaired by grinding, machining, welding, notching, or stamping. Clean all tapped receiving holes and check for thread deterioration.
Confirm that every eye bolt meets the performance requirements for your application.
Tip: Powerful Machinery’s stainless steel eye bolts resist rust and corrosion, making them ideal for marine, outdoor, and chemical environments. Their durability reduces the risk of unexpected failures during the testing process.
Before you begin, complete these safety checks:
Safety Check | Description |
|---|---|
Clean Threads | Ensure threads on the shank and receiving holes are clean. |
Identification Markings | Verify the eyebolt has proper identification markings. |
Proper Seating | Always screw the eye bolt down completely for proper seating. |
Secure Nuts | Tighten nuts securely against the load. |
Thread Engagement | For blind tapped holes, ensure thread engagement is more than 1.5 times the diameter in steel and 2.5 times in aluminum. |
Avoid Damage | Do not use if the eyebolt is bent, damaged, or modified. |
Angle Usage | Avoid using shouldered eyebolts at angles between 45 and 90 degrees to the bolt axis. |
No Modifications | Never repair, replace, or modify an eyebolt. |
Gap Check | Do not use if a gap exists between the part and the eyebolt. |
Hook Size | Do not use a hook larger than the diameter of the eyebolt opening. |
Angular Pulls | Avoid using a plain pattern eye bolt for angular pulls. |
Shock Loading | Shock loading must be avoided. |
Wear and Damage | Never use an eye bolt that shows signs of wear or damage. |
Bent or Elongated | Never use an eye bolt if the eye or shank is bent or elongated. |
Load Rating | Never exceed the load rating. |
Step-by-Step to Test an Eyebolt Anchor
Follow a systematic approach when you test an eyebolt anchor. This method ensures accuracy and safety.
Select a hydraulic pull tester, such as a Hydrajaws, for the testing process.
Attach the tester to the eye bolt and apply a controlled load.
Confirm the actual load capacity of the anchor by gradually increasing the force.
Ensure the anchor bonds correctly with the concrete or substrate.
Watch for any movement. If the anchor shifts even a few millimeters, it fails the test.
Inspect the substrate for cracks or other signs of stress.
Avoid angular loading. Always install the eye bolt according to manufacturer instructions to prevent common failures.
Note: Powerful Machinery’s stainless steel eye bolts provide reliable performance in concrete, steel, and other substrates. Their precision engineering supports consistent results when you test eye bolts in demanding environments.
How to Measure the Pull-Out Force?
You must measure the pull-out force to verify the strength of each eye bolt. Use a calibrated hydraulic pull tester for this task. Attach the tester securely to the eye bolt. Increase the load gradually while monitoring the gauge. Record the peak pull-out force when the eye bolt either fails or reaches its rated capacity.
During this process, look for signs of wear, damage, or deformation. Use visual inspection to spot corrosion, rust, discoloration, pitting, or cracking. Check for movement or instability with a wrench.
Tap the bolt to detect internal cracks. For advanced testing, use ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection to find hidden defects. Load testing helps you assess the bolt’s capacity and identify any deformation or movement.
Tip: Stainless steel eye bolts from Powerful Machinery outperform galvanized alternatives in corrosive environments. Their high-grade alloys, such as 304 or 316, offer superior durability and require less frequent replacement.
Regularly test eye bolts and document your results. This practice helps you maintain compliance and ensures the safety of your team and equipment.
Compliance, Documentation, and Product Selection
Recording Eye Bolt Testing Results
Accurate records help you prove compliance and maintain safety on every project. Assign a unique ID to each eye bolt using hard stamping, vibro-etching, or RFID technology. These methods make it easy to track each component’s history and inspection status.
You should also keep detailed logs of every eye bolt testing session, including the date, inspector’s name, test results, and any corrective actions taken. This approach supports future audits and helps you identify trends or recurring issues.
Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Unique ID Marking | Hard stamping batch ID or suffix for traceability |
Vibro-etching | Alphanumeric codes with minimal material stress |
RFID Technology | Embedded chips for digital tracking and audit trails |
Tip: Always verify that each eye bolt has the manufacturer’s mark, working load limit, and material grade for full traceability.
Choosing Certified Eyebolts from Powerful Machinery
Selecting the right hardware protects your team and equipment. Powerful Machinery’s eye bolts and eye nuts meet strict safety and quality standards. When you choose certified products, you reduce risk and ensure reliable performance. Consider these criteria:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Inspection Requirements | Inspect before each use for bends, cracks, or gouges |
Material Selection | Choose forged alloy, carbon, or stainless steel for your application |
Load Limits | Confirm the working load limit (WLL) matches your needs |
Safety Certifications | Look for compliance with ASME B30.26 and other standards |
Installation Protocols | Ensure full thread engagement and proper seating |
Retirement Criteria | Remove if wear exceeds 10% or if visible damage appears |
You should also consider material composition, diameter, thread size, and finish. Stainless steel options from Powerful Machinery offer corrosion resistance for marine and outdoor use.
Meeting International Standards
International standards set the benchmark for safety and reliability. Powerful Machinery’s products comply with key specifications such as DIN 580, JIS 1168, and ASTM A489-18e1. These standards cover material quality, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy.
You must never exceed the rated load and always use the correct type for your lifting angle. Mill Test Certificates and traceability codes provide proof of compliance.
Specification Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Standard Name | ASTM A489-18e1, DIN 580, JIS 1168 |
Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel |
Requirements | Proof strength, tensile strength, and dimensional accuracy |
Certification | EN 10204 3.1 MTCs, full traceability, chemical and mechanical verification |
Note: Regular eye bolt testing and documentation ensure you meet both company policies and international regulations.
Conclusion
You must prioritize regular eye bolt testing to keep your jobsite safe and compliant. The table below outlines key inspection steps:
Inspection Criteria | Action Required |
|---|---|
Check for cracks, deformation, or visible damage | Inspect before each use |
Ensure proper installation and thread engagement | Inspect before each use |
Remove from service if any visible cracks or deformations are found | Follow safety protocols |
Compliance with ASME B30.26 and OSHA 1910.184 | Adhere to regulatory standards |
Choosing certified, high-quality eye bolts from Powerful Machinery gives you these advantages:
Reliable lifting and secure material handling
Superior durability in harsh environments
Reduced risk of injury and costly damage
Stay informed and follow best practices to protect your team and equipment.
FAQ
How often should you test eye bolts on a construction site?
You should test eye bolts at least once every 6 to 12 months. Increase the frequency if you use them in harsh environments or for critical lifts. Always follow your company’s safety policy and industry standards.
What signs show that an eye bolt needs replacement?
Look for these signs:
Cracks or visible deformation
Corrosion or rust
Damaged threads
Elongated eye
Remove any eye bolt showing these issues immediately.
Can you reuse eye bolts after a failed load test?
No. You must remove any eye bolt that fails a load test from service. Reusing failed hardware increases the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
Do Powerful Machinery eye bolts meet international standards?
Yes. Powerful Machinery eye bolts comply with DIN 580, JIS 1168, and ASTM A489-18e1. You can request certification documents for your records.


