Selecting the right master link sizes for your project keeps your lifting operations efficient and safe. When you measure your load and match it to the proper link, you help prevent accidents and equipment failure. You must inspect your chain sling, use rated hooks, and consult the manufacturer’s load chart before every lift.
Powerful Machinery provides certified master links trusted by professionals worldwide. Rely on our expertise to ensure your lifting assemblies meet strict industry standards and keep your team protected.
Key Takeaways
Select the right master link size based on your load requirements to ensure safety and efficiency.
Always check compatibility between master links, chains, and hooks to prevent rigging failures.
Consider environmental factors like corrosion and temperature when choosing materials for master links.
Perform regular inspections of slings and master links to catch wear or damage before use.
Consult manufacturer specifications and sizing charts to confirm the correct master link for your project.
What Are Master Links?

Master Link Definition
You use master links as the main connecting point in lifting and rigging assemblies. These heavy-duty steel loops join chain slings, wire ropes, and hooks, creating a secure anchor for your lifting operations. Master links come in several shapes, each designed for a specific purpose.
For example, oblong master links provide extra clearance for multi-leg sling assemblies, while pear-shaped links fit snugly with larger hooks and help distribute loads evenly.
Tip: Always check the shape and grade of your master link before starting a lift. The right design ensures safety and efficiency.
Here is a quick overview of common master link types and their uses:
Type of Master Link | Description | Applications | Size Variations |
|---|---|---|---|
Pear-shaped links | Wider at one end for snug hook fits | Single-leg or two-leg sling assemblies | Varies by load requirements |
Ring-shaped links | Circular, permanently closed loops | Single-leg slings, compact lifting setups | Standard sizes for tasks |
Adjustable master links | Allow movement of sub-links for load balance | Varying leg spacing or loading patterns | Adjustable based on setup |
Alloy sub-assemblies | Made from alloy steel for various applications | Single or multi-leg sling configurations | Different sizes available |
Oblong master links | Elongated for even load distribution | Single-leg and multi-leg configurations | ½ inch to 3-1/2 inches |
Why Master Link Sizes Matter?
Choosing the correct master link size is critical for your safety and the success of your project. If you select a link that is too small, you risk overloading the component, which can lead to failure. If you choose a link that is too large, you may face compatibility issues with your chains or hooks.
You must consider several factors when selecting a master link:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Load Capacity | The link must handle the total weight of your load. |
Chain Compatibility | The link must fit the chain or sling you use. |
Rigging Requirements | The link must match your assembly’s configuration and angles. |
Master links come in a range of sizes and working load limits. For example, a ½-inch master link can handle up to 7,400 lbs, while a 3-1/2-inch link supports up to 279,000 lbs. Always match the link size to your load and rigging setup. This practice keeps your lifting operation safe and compliant with industry standards.
Note: Never guess the size. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and load charts for your project.
Powerful Machinery Master Link Features
Alloy Steel Construction
You rely on master links and rings from Powerful Machinery for their unmatched strength and durability. Each link uses high-strength forged alloy steel, which stands up to heavy lifting tasks and harsh environments. The manufacturing process includes rigorous proof testing at 2.5 times the working load limit.
This ensures that master links and rings perform safely under pressure. Protective finishes add excellent corrosion resistance, so you can use these components in marine, construction, or industrial settings without worry.
When you choose master links and rings made from premium alloy steel, you invest in gear that lasts longer and keeps your team safe.
Here is a quick comparison of features that set Powerful Machinery apart:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Material | High-strength forged alloy steel |
Testing | Proof tested at 2.5x working load limit |
Safety Factor | 4:1 margin for error |
Corrosion Resistance | Protective finishes for harsh environments |
Types and Shapes (Oblong, Pear, Ring)
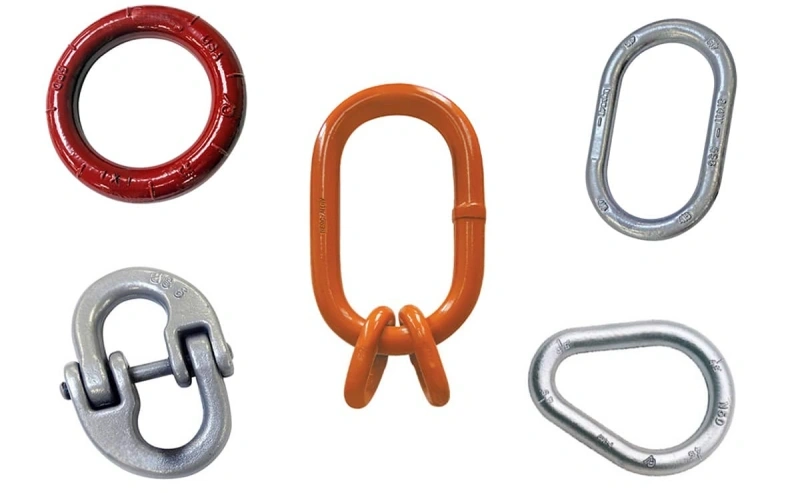

You find a wide selection of master links and rings at Powerful Machinery. Oblong links work best for multi-leg sling assemblies, giving you extra clearance and even load distribution. Pear-shaped links fit larger hooks and help balance single or two-leg slings.
Ring-shaped links offer compact solutions for tight lifting setups. You can also select master link assemblies and coupling links to prevent crane hook crowding and ensure secure connections.
Oblong master links and rings: Ideal for multi-leg slings and heavy loads.
Pear-shaped master links and rings: Perfect for larger hooks and balanced lifts.
Ring-shaped master links and rings: Great for compact, single-leg assemblies.
You match the type and shape to your rigging needs, ensuring every lift meets safety standards.
Certified Safety Standards
Powerful Machinery master links and rings meet strict international safety standards. You benefit from products certified to ASME B30.26, EN 1677, and ISO 8539. These certifications guarantee a high design factor, proof loading, and material quality.
Powerful Machinery uses a traceability framework, assigning unique batch numbers and automating record-keeping. Quality control checks happen at every stage, and regular audits verify compliance. You can trust that every master link and ring meets or exceeds safety standards for lifting operations.
Standard | Description | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
ASME B30.26 | Rigging Hardware | 5:1 design factor, proof loading, temperature |
EN 1677 | Components for Slings | 4:1 design factor, material, mechanical property |
ISO 8539 | Forged Steel Lifting Components | Chain sling components, harmonized with EN |
You protect your team and equipment by choosing master links and rings that comply with global safety standards.
Guide to Choosing Master Link Sizes
Choosing master link sizes for your project requires a systematic approach. You must consider the total load, the configuration of your sling, the compatibility with chain link sizes, and the environment where you will use the equipment.
This how-to guide walks you through each step, helping you select the right master link sizes for safe and efficient lifting.
Load Capacity and Working Load Limit
You start by determining the total load you need to lift. The working load limit of your master link must always meet or exceed the combined load of your sling assembly.
You should never guess the working load limit. Instead, consult Powerful Machinery’s sizing charts and specifications to verify the correct master link sizes for your application.
Calculate the total load, including the weight of the object and any rigging hardware.
Check the working load limit marked on the master link. This value represents the maximum load the link can safely support.
Select master link sizes that match or exceed the working load limit of your sling assembly.
For multi-leg slings, ensure the master link distributes the load evenly across all legs.
Tip: Always use master links with a safety factor of at least 4:1. This margin helps protect against unexpected load shifts or dynamic forces during lifting.
Application and Sling Configuration
The configuration of your sling directly influences your choice of master link sizes. You must identify whether you are using a single-leg, two-leg, three-leg, or four-leg sling. Each setup requires specific master link assemblies to ensure safe load distribution.
When you use a two-leg sling, select a master link that accommodates both legs and fits the crane hook. For three-leg and four-leg slings, choose master link assemblies designed to prevent crowding and maintain proper load alignment.
The application type—such as vertical, choker, or basket hitch—also affects the forces on the master link.
The following table highlights technical details you must consider:
Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
Sling Angle Impact | A horizontal sling angle of 30 degrees doubles the tension on the sling, increasing failure risk. |
Safety Factor Consideration | The rated capacity of the sling decreases sharply with lower sling angles. |
Engineering Review Requirement | A Critical Lift Plan is necessary for lifts with sling angles below 30 degrees, requiring approval from a qualified person. |
Load Verification | Ensure the rated load of rigging equipment matches the number of sling legs and hitch configuration. |
Note: Always verify sling angles and configurations before selecting master link sizes. Incorrect angles can reduce the working load limit and compromise safety.
Chain Link Sizes and Compatibility
You must match master link sizes to the chain link sizes and the dimensions of your crane hook. Proper fitting prevents hardware crowding and ensures safe load transfer. Chain master link compatibility is essential for maintaining the integrity of your lifting assembly.
Master links come in various sizes to accommodate different lifting capacities and crane hook dimensions.
Each size pairs with specific working load limits and is compatible with chain and wire rope slings.
Sub-assemblies help reduce hardware crowding and maintain proper load alignment during lifting.
Proper fitting of master links with crane hooks and other components is crucial to avoid overcrowding.
Overcrowding leads to unusual stress on components, which is not permissible.
The diameter of links must balance strength requirements, as larger links can complicate compatibility with connectors.
Master links must meet specific breaking load factors, ensuring they are strong enough for the intended lifting operations.
The working load limit of the master link must match or exceed the total working load limit of the sling assembly.
Multi-leg slings require specific master link shapes to distribute forces correctly.
The master link must fit properly in the crane hook to prevent component failure.
Tip: Use Powerful Machinery’s chain master link sizing charts to confirm compatibility with your chain link sizes and crane hooks.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental factors play a critical role in selecting master link sizes. You must evaluate the conditions where you will use the lifting equipment. Corrosive environments, extreme temperatures, and exposure to moisture or chemicals can affect the performance and longevity of your master links.
Environmental Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
Corrosive Environments | Use stainless steel (304 or 316 grade) or galvanized steel for rust resistance. |
Temperature Extremes | Opt for heat-treated alloys in high-heat settings; ensure ductility in low temperatures. |
Moisture and Chemical Exposure | Avoid carbon steel; consider coated or non-metallic alternatives. |
You protect your lifting assembly by choosing master link sizes and materials suited to your environment. Stainless steel and galvanized options from Powerful Machinery offer enhanced resistance to rust and corrosion, ensuring reliable performance in marine or chemical settings.
Callout: Always review environmental factors in your how-to guide for master link selection. This step helps you maintain safety and extend the life of your rigging hardware.
By following this guide, you ensure that your master link sizes match your load requirements, sling configuration, chain link sizes, and environmental conditions. You create a lifting assembly that meets industry standards and keeps your team safe.
How to Use Sizing Charts?
Reading Manufacturer Specifications
You must understand manufacturer specifications before ordering alloy steel chain slings for lifting applications. Sizing charts help you select the right master link for your project. You find these charts on Powerful Machinery’s website and product documentation.
Each chart lists the recommended chain diameter, working load limit, and compatible sling configurations. You should always check the chart for your specific applications.
Follow these steps to read a sizing chart:
Identify the type of master link required for your lifting applications.
Locate the recommended chain diameter for your sling assembly.
Find the working load limit that matches your project’s needs.
Confirm the length and width of the master link to ensure proper fit.
Review any notes about environmental factors or special applications.
Tip: Always use the sizing chart when you measure alloy steel chain sling length. This ensures your assembly meets safety standards and fits your equipment.
Interpreting Markings and Dimensions
You see markings and dimensions stamped directly on master links. These markings show the working load limit, chain diameter, and length. You must interpret these details to verify compatibility with your sling and hook.
Here is a table to help you understand common markings:
Marking | Meaning | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
WLL | Working Load Limit | Ensures safe lifting |
Dia | Chain Diameter | Matches sling and link size |
Length | Overall Link Length | Fits your lifting assembly |
You should always compare the markings with the sizing chart before using master links in your applications. This step helps prevent mismatches and ensures your lifting operations run smoothly.
Note: If you have questions about sizing or compatibility, contact Powerful Machinery’s technical support for expert guidance.
Common Mistakes in Master Link Selection
Overlooking Safety Ratings
You must always check safety ratings before you select master links for your rigging. The master link acts as the keystone in your rigging assembly. It transfers the power from your lifting machine to the load. If you ignore safety ratings, you risk a complete failure of your rigging system.
This mistake can cause equipment damage and put your team in danger during lifting operations. You should never assume a master link is strong enough for your rigging. Always look for certified markings and verify the working load limit. You protect your rigging and lifting operations by following safety standards.
Safety Tip: Always inspect the master link for clear safety markings before you start any lifting operations.
Ignoring Chain Master Link Compatibility
You need to match the master link size to your chain and hook dimensions. Many rigging failures happen when you use incompatible components. If the master link does not fit the chain or hook, you create weak points in your rigging.
These weak points can lead to uneven load distribution and sudden failure during lifting operations. You should always use sizing charts from Powerful Machinery to confirm compatibility. Proper fit keeps your rigging secure and your lifting operations efficient.
Check the diameter of the chain.
Verify the master link fits the crane hook.
Use only compatible components in your rigging.
Misjudging Environmental Impact
You must consider the environment where you use your rigging. Corrosive settings, extreme temperatures, and moisture can weaken master links. If you ignore these factors, you shorten the lifespan of your rigging and increase the risk of failure during lifting operations.
You should select master links made from materials that resist rust and corrosion. Stainless steel and galvanized options from Powerful Machinery offer extra protection for your rigging in harsh environments.
Environmental Factor | Impact on Rigging | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Corrosion | Weakens links | Use stainless steel or galvanized master links |
Temperature extremes | Reduces strength | Choose heat-treated alloy steel master links |
Moisture | Causes rust | Store rigging in dry areas and inspect it often |
Note: Always review environmental conditions before you choose master links for your rigging. This step helps you maintain safe lifting operations.
Safety and Inspection Guide
You must prioritize safety every time you use slings and master links. Proper inspection routines and timely replacement of worn components help you maintain the strength and reliability of your lifting assemblies.
Powerful Machinery recommends a structured approach to safety, ensuring your equipment performs at its best and protects your team.
Pre-Use Safety Checks
Before you use any sling or master link, you need to perform a thorough safety check. This step helps you catch problems early and avoid dangerous situations. Always clean your slings before inspection so you can see any hidden damage. Place the chain sling on a flat surface or hang it until fully stretched.
Untwist any twisted sections to check the true condition of the sling. Make sure the identification tag is present and easy to read. Examine every part of the sling, including the master link, load pins, and hooks.
Here is a table to guide your pre-use safety checks:
Safety Check Item | Description |
|---|---|
Inspect links | Examine every link, master link, load pin, and hook for cracks, breaks, or excessive wear. |
Identification tags | Look for missing or unreadable identification tags. |
Surface damage | Identify nicks, gouges, or surface damage. Remove the sling from service if you find any cuts, burns, or deep scratches. |
Elongation | Check for stretched or elongated links and components. If you see any, do not use the sling. |
Corrosion | Inspect for rust, corrosion, or weld splatter. |
Hook condition | Make sure all links move freely and that hooks are not twisted or opened beyond safe limits. |
Tip: If you find any sign of wear or defect, remove the sling from service immediately. Never use a sling or master link that does not meet safety standards.
Inspection Intervals
You need to inspect your slings and master links regularly to maintain safety. Initial inspections must happen before you use new slings for the first time. In high-use environments, you should check your slings daily, weekly, or at the start of each shift.
For most lifting operations, you must schedule periodic inspections every 6 to 12 months. If your equipment works in severe conditions, increase the inspection frequency to monthly or quarterly.
Inspect chain slings before first use.
Perform frequent inspections daily, weekly, or per shift, depending on usage and regulations.
Schedule periodic inspections every 6 to 12 months, including thorough functional testing.
Increase inspection frequency to monthly or quarterly for equipment in harsh environments.
Arrange special inspections after any incident, repair, or suspected damage.
Customize your inspection schedule as advised by qualified personnel.
Powerful Machinery recommends you keep detailed records of each inspection. Note the manufacturer, load limit, sling type, and previous inspection dates. This practice helps you track the safety and condition of your slings over time.
Note: Regular inspection is essential for identifying weakening or damage. Consistent routines help you catch problems before they lead to failure.
Replacement Guidelines
You must know when to replace your slings and master links to maintain safety. Several key indicators tell you when a component no longer meets safety requirements. If you see visible deformation, excessive wear, or elongation, remove the sling from service.
Damaged or missing components, such as hooks or identification tags, also require immediate replacement. Signs of corrosion or cracking mean the sling or master link has lost its strength and should not be used.
Replace any sling or master link with visible deformation.
Remove slings showing excessive wear or elongation.
Discard equipment with damaged or missing components.
Replace slings and master links with signs of corrosion or cracking.
If hooks are open more than 15% of the standard throat opening or twisted more than 10° from the normal plane, replace them immediately.
Remove any sling that appears stretched when measured.
Never attempt to repair a damaged master link or sling yourself. Always use certified replacements from Powerful Machinery.
Safety Alert: Always follow manufacturer guidelines for replacement. Using worn or damaged slings and master links puts your team and equipment at risk.
By following these safety practices, you ensure your slings and master links deliver reliable performance and maintain the strength needed for every lift. Regular inspection and timely replacement keep your lifting operations safe and efficient.
Conclusion
You ensure safe lifting by following these steps:
Select the right chain sling based on load, grade, and environment.
Match sling configuration to your project’s stability needs.
Confirm compatibility using manufacturer charts.
Certified master links from Powerful Machinery offer unmatched safety and legal compliance:
Aspect | Certified Chains | Uncertified Chains |
|---|---|---|
Safety | Rigorous testing | Risk of failure |
Material Quality | High-grade alloy steel | Lower-quality materials |
Explore Powerful Machinery’s website for expert guides, safety rules, and standards to support your selection.
FAQ
How do you determine the correct anchor chain size for your project?
You select the anchor chain size by considering the total load, anchor type, and application requirements. Always check manufacturer charts and standards to ensure the anchor chain size matches your master link and lifting assembly.
What is the recommended anchor chain length for safe lifting operations?
You calculate anchor chain length based on the distance between the anchor point and the load. Manufacturer guidelines and standards help you choose the anchor chain length that ensures safe operation and proper tension in your master link setup.
Why must you follow standards when selecting a master link?
You follow standards to guarantee safety, reliability, and legal compliance. Standards define the minimum requirements for master link strength, material, and testing. Adhering to standards protects your team and equipment during anchor and lifting operations.
Can you use any anchor with any master link?
You must match the anchor and master link according to size, load rating, and compatibility. Using mismatched components can cause failure. Always consult the manufacturer specifications and standards before connecting an anchor to a master link.
How often should you inspect your master link and anchor chain?
You inspect your master link and anchor chain before each use and at regular intervals. Frequent inspections help you identify wear, corrosion, or damage. Following standards and manufacturer recommendations ensures your anchor and master link remain safe.


