You use lifting magnets to move heavy ferrous materials by harnessing the strong magnetic force. This process lets you lift steel plates, blocks, and other metal objects without physical contact.
Different types of lifting magnets exist for specific tasks. The table below highlights the main types and where you might see them most often:
Type of Lifting Magnet | Market Share Insights |
|---|---|
Electromagnetic Lifting Magnets | Superior capacity, popular in automotive and industrial sectors. |
Permanent Lifting Magnets | Cost-effective, common in construction and manufacturing, and no external power needed. |
Battery-Operated Lifting Magnets | Flexible for locations without power, adaptable for many uses. |
Manual Lifting Magnets | Simple and portable, best for smaller operations. |
Choosing the right lifting magnet ensures safe and efficient handling in your workplace.
Key Takeaways
Lifting magnets use a strong magnetic force to move heavy metal objects without physical contact, making them efficient tools in various industries.
Choose the right type of lifting magnet based on your needs: permanent magnets are cost-effective, while electromagnets offer adjustable strength.
Always ensure the surfaces are clean and flat for maximum grip; dirt or rust can significantly reduce lifting capacity.
Regular maintenance is crucial for safety and performance; inspect and clean magnets before each use to prevent accidents.
Understand the lifting capacity factors, such as material type and thickness, to select the appropriate magnet for your lifting tasks.
Science of Lifting Magnets

Magnetic Force Explained
When you use lifting magnets, you rely on the invisible force of magnetism to move heavy metal objects. This force comes from the magnetic field, which pulls ferrous materials like steel toward the magnet.
The strength of this pull depends on the size of the magnet, the area in contact, and the intensity of the magnetic field. You can see how these factors work together in the table below:
Concept | Description |
|---|---|
Magnetic Force | The force between magnets depends on the magnetic field and the area of the magnets. |
Magnetic Pressure Formula | P_{mag} = frac {B^{2}}{2mu_{0}} where P_{mag} is the force per unit area in pascals. |
Types of Magnets | Includes permanent magnets, electromagnets, ferromagnetism, diamagnetism, and superconducting magnets. |
Lifting Forces | Must provide an upward force to counteract gravity. |
Stability | Ensures the system does not slide or flip, neutralizing lift. |
You need to make sure the lifting magnet creates enough upward force to overcome gravity. Stability also matters. If the magnet or the load shifts, you could lose the lift. Always check that the magnet sits flat on the material for the best grip.
Tip: Clean surfaces help maximize magnetic force. Dust or rust can weaken the connection.
Magnet Strength Measurement
You measure the strength of a lifting magnet using several key parameters. Each one tells you something different about how well the magnet will perform in real-world tasks. Here is a quick overview:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Magnetic Field Strength | The intensity of the magnetic field produced by the magnet. |
Magnetic Flux Density | The amount of magnetic flux through a unit area. |
Coercivity | The resistance of a magnet to becoming demagnetized. |
Magnetic Moment | A measure of the strength of the magnet’s magnetic field. |
Pull Force | The maximum weight the magnet can lift. |
Saturation Magnetization | The maximum magnetization a material can achieve under an external field. |
When you select lifting magnets for your job, look at the pull force rating first. This number tells you the maximum weight the magnet can safely lift. Other measurements, like magnetic field strength and coercivity, help you understand how the magnet will perform over time and in different environments.
Types of Lifting Magnets
You will find several types of lifting magnets in industrial settings. Each type uses a different working principle to move heavy metal objects. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right tool for your job. The table below gives you a quick comparison of the main types of magnet lifters:
Type of Lifter | Working Principle | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
Permanent Magnetic Lifters | Use a magnetized core to create a constant magnetic field. You engage or disengage with a lever. | No power needed, portable, low maintenance | Lower lifting capacity, less effective on rough surfaces |
Electromagnet Lifters | Generate force by passing an electric current through coils. You can adjust the magnetic strength. | High lifting capacity, adjustable, good for industry | Needs continuous power, higher cost, and safety risks during outages |
Electro-permanent Lifters | Combine permanent and electromagnets. You control the force with a short electric pulse. | Efficient, holds load without power, safe | More complex, performance can drop if power is lost |
Permanent Magnetic Lifters

Permanent magnetic lifters use a powerful magnetized core to create a steady magnetic field. You activate or deactivate the magnet by moving a manual lever.
This design means you do not need electricity to operate the lifter. You can use these heavy-duty magnets in places where power is not available or where you want to avoid the risk of power failure.
Note: Permanent magnetic lifters work best on clean, flat surfaces. Dirt or rust can reduce their grip.
The permanent magnet lifter from Powerful Machinery stands out in this category. It uses high-performance Nd-Fe-B magnets, which give you strong and reliable lifting power. You do not need slings, hooks, or cables, so you reduce workplace hazards.
The lifter does not rely on an external power source, so you never have to worry about dropped loads during a power outage. Its compact design lets you operate it with one hand, making your work faster and safer. You can lift steel plates, blocks, and molds with ease.
The safety lever and advanced magnetic circuit add extra protection for you and your team. This permanent magnetic lifter also streamlines your workflow by needing fewer operators, which boosts your efficiency.
Electromagnet Lifters
Electromagnetic lifters use electric current to create a magnetic field. When you turn on the power, current flows through coils of wire inside the magnet. This process generates a strong magnetic force that can lift very heavy loads.
You can adjust the strength of the magnet by changing the amount of current. These heavy-duty magnets are common in factories, scrap yards, and shipyards where you need to move large steel plates or beams.
You must keep the power on while lifting. If the power goes out, the magnet loses its grip, which can be dangerous. Electromagnet lifters often cost more to operate because they use electricity and need regular maintenance.
Electro-permanent Lifters
Electro-permanent lifting magnets combine the best features of permanent and electromagnet lifters. They use two sets of magnets: one set creates a constant magnetic field, and the other set can be switched on or off with a short electric pulse. You only need power to change the magnet’s state, not to keep it holding the load. This design makes these heavy-duty magnets both efficient and safe.
You can use electro-permanent lifters in places where you want the security of a permanent magnet but also need the flexibility to control the magnetic force. These types of lifting magnets are popular in automated production lines and robotic systems. They hold the load even if the power fails, which adds an extra layer of safety.
Tip: Always match the type of lifting magnet to your specific job. Consider the weight, shape, and surface of the material you need to lift.
You will see these types of lifting magnets used in many industries, such as construction, manufacturing, marine, and logistics. Each type offers unique benefits, so you can find the right solution for your lifting needs.
How Does a Lifting Magnet Work?
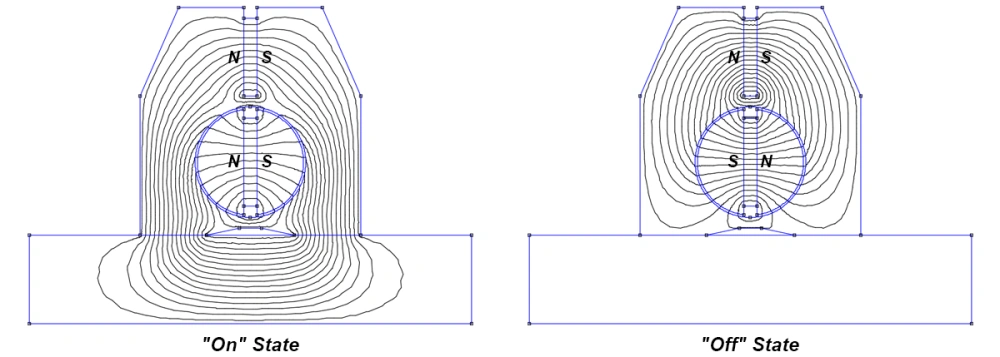
Permanent Magnet Operation
You use permanent lifting magnets to move ferrous materials by relying on a magnetized core. The magnet lifting process starts when you place the lifting magnet directly onto the steel plate or block. The magnetic field flows from the magnet into the metal, creating a strong grip.
You activate or deactivate the magnetic force with a simple lever. This action aligns the internal magnetic domains, allowing the lifting magnet to hold or release the load.
Permanent magnetic lifters do not need electricity. You get consistent performance and safety because the magnetic force remains stable. You can use these lifting devices in areas without power.
The permanent magnet lifter from Powerful Machinery uses high-performance Nd-Fe-B magnets. You operate it with one hand, making magnet lifting tasks easier and safer. The safety lever ensures the lifting magnet does not release unexpectedly.
You should always check that the surface of the ferrous materials is clean and flat. This step helps maximize the grip and lifting capacity.
Permanent lifting magnets maintain their force even during power failures. You do not face risks from sudden outages. The table below shows how safety mechanisms differ among lifting magnets:
Type of Magnet | Safety Mechanism | Power Dependency |
|---|---|---|
Permanent Magnet | Maintains magnetic force without power; no risk of power failure affecting safety | Not dependent on power |
Electromagnet | Requires electricity; switches off automatically during power failure, reducing risks | Dependent on power |
Electro-permanent Magnet | Retains magnetic force without power; ensures safety during power interruptions | Not dependent on power |
Electromagnet Operation
You use an electromagnet lifter when you need to lift heavy ferrous materials in industrial settings. The lifting magnet works by passing an electric current through coils inside the device.
When you switch on the power, the coils generate a magnetic field. This field flows into the metal object, allowing magnet lifting to occur.
You can adjust the strength of the lifting magnet by changing the amount of current. This feature gives you flexibility for different lifting devices and load sizes. Electromagnetic lifters are common in factories and scrap yards. You must keep the power on during the entire lifting process.
If the power fails, the lifting magnet releases the load. Some lifting electromagnet models include battery packs for emergencies, so you can maintain operation until power returns.
Electromagnets can be turned off instantly. You do not have to worry about residual magnetism. This feature helps you handle ferrous materials safely and efficiently.
You should always monitor the power supply when using electromagnet lifters. This step helps prevent accidental drops and ensures safe operation.
Electro-permanent Magnet Operation
You use electro-permanent lifting magnets when you want precise control and maximum safety. These lifting magnets combine permanent and electromagnet technology. The magnet lifting process uses two types of magnetic materials: magnetically hard (Nd-Fe-B) and semi-hard (Alnico).
The operation follows these steps:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Use of electro-permanent magnet technology with two types of magnetic materials: magnetically hard (Nd-Fe-B) and semi-hard (Alnico). |
2 | Application of an instantaneous electric current to control the magnetic state, allowing for lifting or releasing ferrous materials. |
3 | When a current pulse of a certain polarity is applied, it aligns the materials to enhance the external magnetic flux. |
4 | Applying a current pulse of the opposite polarity reverses the magnetization of the semi-hard material, decreasing the external magnetic flux. |
5 | This process allows for precise control of magnetic fields for various applications. |
You only need electricity to change the magnetic state. The lifting magnet holds the load even if the power goes out. You get absolute safety because the magnetic force does not disappear during power interruptions.
Electro-permanent lifting magnets are popular in automated production lines and robotic lifting devices. You can lift and release ferrous materials with high precision.
Electro-permanent lifting magnets ensure safety by not losing magnetic force during power failures. You can rely on them for critical lifting tasks.
You see lifting magnets used in many industries. You can choose the right lifting devices for your needs by understanding how each lifting magnet operates.
Components of a Lifting Magnet
Magnet Materials
You will find that the materials used in lifting magnets play a big role in how well they perform. Manufacturers often choose between aluminum and copper for the windings inside industrial lifting magnets. Each material brings its own strengths and weaknesses to the table.
Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum | Lighter weight, increased speed, less wear on carriers, and industry standard | May not have the same lift capacity as copper |
Copper | Excellent for overhead cranes, no capacity limits | Not cost-effective for scrap processing |
Aluminum-wound magnets help you move loads faster and reduce wear on your equipment. You will notice that these magnets are lighter, which makes them easier to handle.
Copper-wound magnets, on the other hand, work best for overhead cranes because they can handle higher capacities. The choice of material affects both the efficiency and the lift capacity of your magnet. When you need a strong magnetic path for heavy-duty lifting, the right material ensures reliable performance.
Control Mechanisms
Control mechanisms give you the ability to operate lifting magnets safely and precisely. You can turn the magnetic force on or off in electromagnets, which lets you pick up and release loads with high control.
Adjusting the current allows you to match the lifting capacity to the size of your load. Electro-permanent magnets only need electricity for the initial magnetization, so your load stays secure even if the power goes out.
Modern lifting magnets often include extra safety features:
Fail-safe designs keep your load secure during power interruptions.
Sensors and diagnostics monitor the system for safe operation.
Individual gripper control lets you handle materials with precision.
Automatic detection of anomalies can stop operations to prevent accidents.
These features help you maintain a consistent magnetic clamping force and improve workplace safety. With the right control mechanisms, you can trust your lifting magnet to perform reliably in demanding environments.
Performance Factors
Lifting Capacity
You need to understand what affects the lifting capacity of a magnet before you start any job. Several factors play a role in how much weight a lifting magnet can handle. The table below shows the most important ones:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Material Type | Mild steel is preferred for its higher ability to conduct magnetism compared to alloy steels. |
Steel Thickness | Thicker steel allows better penetration of the magnetic field, ensuring maximum lifting capacity. |
Air Gaps | Any air gap reduces performance; rust, dirt, or ice can create these gaps. |
Temperature | High temperatures can demagnetize the lifting magnets, reducing their effectiveness. |
Number of Magnets | More magnets are needed for larger loads to ensure efficient lifting. |
You should always consider lifting capacity and load considerations when choosing a magnet. If you use an electromagnet lifter, you can adjust the strength for different weights. This flexibility helps you match the magnet to your specific needs.
Material and Surface
The condition of the material and its surface has a big impact on how well your lifting magnet works. You want to make sure the magnet has the best possible contact with the metal. Here are some key points to remember:
An air gap between the magnet and the material greatly reduces lifting force. Even small gaps from rust, paint, or dirt can cut holding strength by half or more.
Smooth, clean surfaces allow maximum magnetic contact.
Surface flatness is equally important; a magnet gripping a flat steel plate will hold much more securely than one contacting a rough or uneven surface.
Poor contact reduces the effective magnetic area and weakens the lift.
Non-magnetic layers like oil, scale, or plating create separation between the magnet and the steel, lowering performance.
If you use an electromagnet lifter, always check the surface before lifting. Clean and flat surfaces help you get the most out of your equipment.
Temperature Effects
Temperature can change how your lifting magnet performs. High heat may weaken the magnet and lower its lifting power. The table below shows safe temperature ranges for lifting magnets in different settings:
Maximum Operating Temperature | Application Description |
|---|---|
Up to 200°C (392°F) | Standard operating range for many high-temperature lifting magnets is suitable for moderate levels. |
Up to 300°C (572°F) | Used in foundries and high-temperature processes where materials are elevated but not extreme. |
Up to 500°C (932°F) | Necessary for extremely high-temperature environments, made with specialized materials to maintain performance. |
If you use an electromagnet lifter in a hot environment, always check the temperature rating. Some magnets can handle higher temperatures, but others may lose strength or even fail.
You should match your magnet to the job’s temperature demands to keep your operation safe and efficient. Remember, an electromagnet lifter gives you more control in changing conditions, but you still need to respect its limits.
Applications of Lifting Magnets
Industrial Uses
You will find lifting magnets in many industries that handle heavy metal materials. In construction, you use them to move steel beams, plates, and rebar safely and quickly. Marine operations rely on lifting magnets to load and unload steel cargo or ship components.
Transportation companies use them to handle metal sheets and parts in warehouses and shipping yards. Cargo handling at ports often involves lifting magnets to transfer steel containers and machinery.
These applications help you save time and reduce manual labor. You also improve safety by minimizing the need for slings or hooks.
Lifting magnets work well in industrial settings where you need to move large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped ferrous objects. You can use them for both flat and cylindrical materials, making them versatile tools for many tasks.
Powerful Machinery Solutions
When you need reliable solutions for industrial lifting applications, the permanent magnetic lifter from Powerful Machinery stands out.
You can use this tool for a wide range of application scenarios, including lifting steel sheets, blocks, rods, and cylinders. The design focuses on safety and efficiency, with a robust build that handles harsh industrial conditions.
The permanent magnet lifter offers a safety factor of at least 2.5, giving you confidence during heavy lifting. You can operate it easily with a release mechanism and a turnable handle. Some models allow you to lift both flat and cylindrical surfaces, which increases your flexibility in different application settings.
Here is a table showing the main features and specifications of several models:
Model | Lifting Capacity (kg) | Weight (kg) | Max Load (kg) | Dimensions (mm) | Safety Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PML10 | 1000 | 264 | 3500 | 168 x 168 x 266 | <80 |
PML15 | 1500 | 353 | 5250 | 172 x 168 x 380 | <80 |
PML20 | 2000 | 378 | 7000 | 230 x 217 x 462 | <80 |
PML30 | 3000 | 453 | 10500 | 290 x 265 x 567 | <80 |
PML50 | 5000 | 647 | 17500 | 290 x 265 x 707 | <80 |
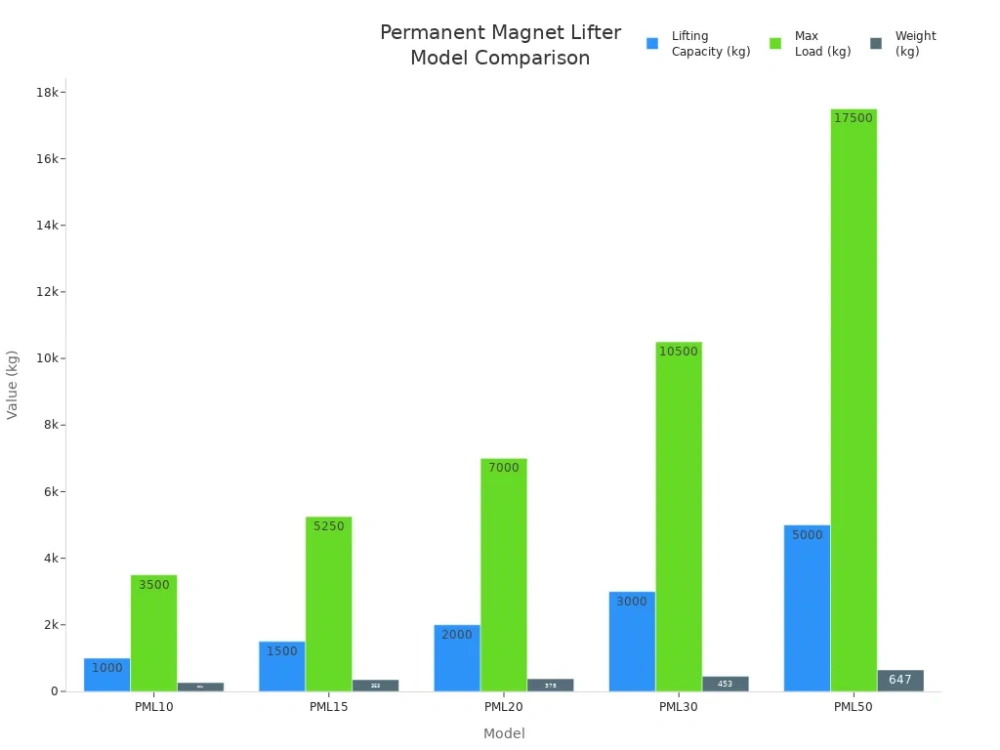
You can trust the permanent magnetic lifter for demanding application needs in factories, docks, and warehouses. Its strong grip, easy operation, and high safety factor make it a valuable asset for your industrial lifting applications.
Safety with Lifting Magnets
Risks and Precautions
When you operate lifting magnets, you must always keep safety at the top of your mind. The main hazard comes from falling materials if the magnet loses its grip. This can happen because of power loss, improper use, or unsuitable load conditions.
To reduce risks, you should follow these safety considerations for working with magnet lifters:
Read and understand all instructions before using any lifting magnet.
Only allow authorized personnel to operate lifting magnets.
Inspect the magnet before and after each use.
Make sure you have a safety factor of at least 3:1 for every lift.
Stay clear of the load while it is being lifted or moved.
Never stand under a load carried by a lifting magnet.
Use a spreader bar when lifting large plates.
Move and lower loads gently to avoid sudden shifts.
Tip: Always check the magnetic properties and surface profile of the load. Not all steel types or shapes are suitable for magnetic lifting.
You should also look for equipment with warning devices that show when the magnet is active or if power is low. Some systems require two control actions to release a load, which helps prevent accidental drops. These steps help you avoid accidents and keep your workplace safe.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps your lifting magnets reliable and extends their lifespan. You should follow these steps to ensure safe operation:
Inspect the magnetic surface for wear, cracks, or damage before each use.
Clean the magnet regularly to remove metal particles and dust.
Lubricate moving parts to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation.
Distribute the load evenly across the magnet’s surface for maximum grip.
Replace or repair damaged parts right away to avoid further problems.
Use lifters designed for your specific environment, such as high temperatures or dusty areas.
Handle magnets carefully and avoid dropping them on rough surfaces.
Regular inspections and proper cleaning help you spot issues early and prevent equipment failure.
By following these maintenance tips, you help ensure that your lifting magnets remain safe and effective for every job.
Choosing a Lifting Magnet
Selection Criteria
When you select a lifting magnet, you need to match the tool to your specific job. Start by defining your application requirements. Think about what you need to lift, the environment, and the strength needed. The table below shows important criteria you should consider:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Define Application Requirements | Know the purpose, environment, and key needs like field strength, temperature, and durability. |
Select the Right Magnetic Material | Choose materials such as NdFeB for strong fields or SmCo for high temperatures. |
Determine Optimal Shape and Dimensions | Pick a shape that fits your space and focuses the magnetic field where needed. |
Simulate Magnetic Field Distribution | Use simulations to predict how the magnet will perform. |
Test the Design in Real-World Conditions | Make sure the magnet works well in your actual environment. |
Optimize for Sustainability and Cost Efficiency | Look for designs that use sustainable materials and are cost-effective. |
You also need to check material compatibility.
Make sure the load is ferromagnetic, like steel or iron.
The surface should be clean and flat for the best grip.
Consider the temperature and humidity where you will use the magnet.
When you want to know how to choose the right magnet lifter, look at these product specifications:
Control options, such as manual or remote.
Magnetizing and demagnetizing time.
Customization and accessories.
International standards and certifications.
Load handling, including surface and material.
Maintenance and servicing needs.
Safety features.
Brand Considerations
You want a brand that stands for safety and reliability. Look for certifications like ASME breakaway testing, CE, and EN 13155:2020(E). These show the magnet meets strict safety and quality standards.
Brands should provide full documentation and certificates of conformance. Annual pull-off tests help ensure the magnet stays reliable.
Powerful Machinery offers certified lifting magnets trusted in industrial settings. You get products that meet or exceed international standards, giving you peace of mind for every lift. Their permanent magnet lifters combine strong performance with proven safety, making them a smart choice for your lifting needs.
Conclusion
You have seen how lifting magnets play a vital role in industries like manufacturing, construction, and recycling. Each type offers unique benefits, but safety and performance always come first.
Always wear eye protection and follow safety guidelines when handling magnets.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Reliability | Designed for ferromagnetic materials, ensuring effective operation. |
Energy Efficiency | Requires no external power source, making it cost-effective for continuous operations. |
Safety Features | Emphasizes proper usage precautions and maintenance to enhance safety in industrial settings. |
Choose the permanent magnetic lifter from Powerful Machinery for reliable, certified lifting solutions. For special projects, consult with experts to find the best fit.
FAQ
What materials can you lift with a lifting magnet?
You can lift ferrous materials like steel and iron. Lifting magnets do not work on non-magnetic metals such as aluminum, copper, or stainless steel with low magnetic properties.
How do you maintain a lifting magnet for best performance?
You should clean the magnet surface regularly. Inspect for damage or rust before each use. Store the magnet in a dry place. Lubricate moving parts as needed to keep the mechanism smooth.
Can you use a permanent magnetic lifter without electricity?
Yes, you can use a permanent magnetic lifter without any power source. The magnet uses a strong internal core to create a magnetic field, so you do not need electricity for operation.
What safety steps should you follow when using lifting magnets?
Always check the load’s weight and surface condition. Never stand under a suspended load. Use only trained operators. Inspect the magnet before each lift to ensure safe operation.
How long does a lifting magnet last?
With proper care, a lifting magnet can last over ten years. Regular cleaning and inspection help maintain its strength and reliability for daily industrial use.


