Key Differences in Hook Design
Explore the essential features of rebar and snap hooks.
Features | Rebar Hook | Snap Hook |
|---|---|---|
Gate Opening | Large for oversized anchors | Small for standard D-rings |
Typical Use | Rebar, scaffolding, structural steel | Harnesses, lanyards, fixed points |
Profile | Bulky and robust | Compact and lightweight |
Locking Mechanism | N/A | Automatic locking for safety |
Durability | High strength steel construction | Corrosion-resistant finish |
Applications | Fall protection in construction | Versatile across multiple industries |
Ease of Use | Quick attachment in tight spaces | Fast connections to standard gear |
Safety Standards | N/A | Meets ANSI Z359.1-2007 |
The main difference between a rebar hook and a snap hook lies in their design and application. You often see rebar hooks with a larger gate opening, which makes them ideal for connecting to larger anchor points like scaffolding or rebar.
Snap hooks, on the other hand, offer a more compact profile and strict ANSI Z359.1-2007 safety standards, as shown below:
Feature | Snap Hooks | Rebar Hooks |
|---|---|---|
Gate Strength | 3,600 lbs | N/A |
Load Capacity | 5,000 lbs (spine) | N/A |
Choosing the right hook ensures safety and prevents workplace accidents. The rebar hook vs snap hook decision depends on your specific job site needs.
Key Takeaways
Rebar hooks are ideal for large anchor points like scaffolding and rebar due to their large gate openings, ensuring quick and secure connections.
Snap hooks are compact and versatile, perfect for standard D-rings and harnesses, making them suitable for various industries including construction and manufacturing.
Always check safety standards and ensure your chosen hook meets ANSI and OSHA requirements to prevent accidents and ensure reliable performance.
Inspect your hooks regularly for wear and functionality, especially the locking mechanisms, to maintain safety during use.
Choose the right hook based on your work environment: rebar hooks for oversized anchors and snap hooks for standard connections.
Rebar Hook Overview

Design & Features
Rebar hooks stand out for their large gate openings and robust construction. You will notice that these hooks are designed to connect easily to oversized anchor points, such as rebar assemblies and scaffolding.
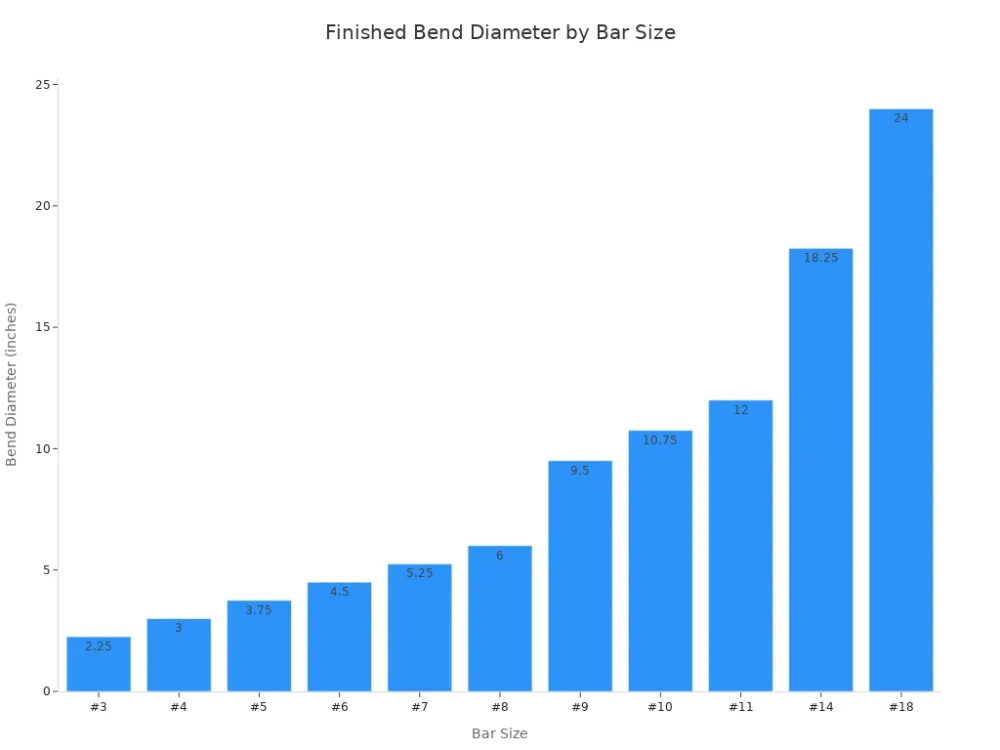
The gate opening allows for quick attachment, even when you wear gloves or work in challenging environments. Industry standards specify precise dimensions for rebar hooks, ensuring compatibility and safety across various bar sizes:
Bar Size | Finished Bend Diameter (D in.) | 90° Hook (ft-in) | 135° Hook (in.) |
|---|---|---|---|
#3 | 0-02 ¼ | 0-04 | 0-04 |
#4 | 0-03 | 0-06 | 0-04 ½ |
#5 | 0-03 ¾ | 0-07 | 0-05 ½ |
#6 | 0-04 ½ | 0-08 | 0-08 |
#7 | 0-05 ¼ | 0-10 | 0-09 |
#8 | 0-06 | 0-11 | 0-10 ½ |
#9 | 0-09 ½ | 1-03 | 0-11 ¾ |
#10 | 0-10 ¾ | 1-05 | 1-01 ¼ |
#11 | 1-00 | 1-07 | 1-00 ¾ |
#14 | 1-06 ¼ | 2-03 | 1-09 ¾ |
#18 | 2-00 | 3-00 | 2-04 ½ |
Manufacturers often use advanced materials to enhance performance. For example, fiberglass reinforced polymer (FRP) provides strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance. Glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic (GFRTP) offers flexibility and sustainability, which can improve durability in harsh environments.
Material Type | Key Properties | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
Fiberglass Reinforced Polymer (FRP) | Strength, Light Weight, Corrosion Resistance | Essential for durability in harsh environments |
Glass Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic (GFRTP) | Enhanced Flexibility, Sustainability | Potential to revolutionize construction with improved performance |
Common Uses
You will find rebar hooks most often on construction sites where workers need to secure themselves to large anchor points. These hooks excel in fall protection systems, especially when you work on scaffolding, steel frameworks, or rebar assemblies.
Their large gate opening makes them ideal for quick, secure connections in dynamic environments.
Tip: Always inspect your rebar hooks before use to ensure the gate and locking mechanism function properly.
When to Choose?
Choose rebar hooks when your job requires frequent attachment to oversized or irregular anchor points. These hooks provide a secure connection in environments where standard snap hooks may not fit. If you work at height or in areas with exposed rebar, rebar hooks offer the versatility and safety you need.
However, you should remain aware of potential safety incidents, such as cuts, abrasions, slips, and strains. Always follow site safety protocols and use proper protective equipment to minimize risks.
Snap Hook Overview

Design & Features
You will notice that snap hooks offer a compact and versatile connector for many safety systems. Their design includes several opening mechanisms, such as slide bolts, triggers, and gates, which provide secure closure and easy operation.
You can select from rigid or swivel configurations, depending on your application needs. Manufacturers offer a range of eye shapes—rectangular, oval, and round rings—to fit different strap types and anchorage points.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Opening Mechanisms | Slide bolt, trigger, and gate mechanisms for secure closure. |
Configurations | Rigid and swivel types for different applications. |
Eye Shapes | Rectangular, oval, and round rings for various strap types. |
Snap hooks often feature automatic locking mechanisms. These mechanisms reduce the risk of accidental disengagement, which is crucial for user safety. You benefit from high-strength materials and corrosion resistance, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments.
Tip: Always check the locking mechanism before each use to confirm it engages properly.
Common Uses
You will find snap hooks in a wide range of industries. In construction, you use them to secure tools and safety harnesses at heights. They help manage rigging systems for hoisting materials and attach cables or wires for stability.
In manufacturing, you connect fixtures, tools, or safety equipment on assembly lines. Aerospace and automotive sectors rely on snap hooks to secure cargo, equipment, and harnesses.
Industry | Application Description |
|---|---|
Construction | Secure tools and safety harnesses at heights. |
Construction | Manage rigging systems for hoisting materials. |
Construction | Attach cables and wires for stability. |
Manufacturing | Connect fixtures, tools, or safety equipment in assembly lines. |
Aerospace | Secure cargo, equipment, and tools for safety and access. |
Automotive | Used in safety harnesses and securing cargo in vehicles. |
Snap hooks must meet strict safety standards, including a minimum tensile strength of 5,000 lbs and gate face load of 3,600 lbs.
When to Choose?
You should choose snap hooks when your job requires frequent, secure connections to standard anchor points. These hooks excel in environments where compact size and quick operation matter.
Evaluate the material, strength, and compliance with safety standards before selecting a snap hook for your job site. If you need a lightweight, reliable connector for harnesses, tools, or cargo, snap hooks provide the right balance of safety and convenience.
Material: Select a snap hook made from durable, corrosion-resistant materials.
Strength: Confirm the load capacity matches your safety requirements.
Safety Standards: Ensure compliance with ANSI and OSHA guidelines.
Never connect snap hooks directly to webbing, rope, or cable unless designed for that purpose. Always follow manufacturer instructions for safe use.
Rebar Hook vs Snap Hook Comparison
Design Differences
When you compare rebar hook vs snap hook, you notice clear differences in their design. Rebar snap hooks feature a large gate opening, which allows you to connect easily to oversized anchorage points such as rebar, scaffolding, or structural steel.
This design makes them ideal for situations where you need to secure your fall arrest system to irregular or bulky structures. Snap hooks, on the other hand, have a more compact profile.
You use them for standard anchorage points and for connecting to harnesses, lanyards, or other equipment. The smaller gate opening fits well with D-rings and fixed points on your fall protection system.
Feature | Rebar Snap Hooks | Snap Hooks |
|---|---|---|
Gate Opening | Large, fits oversized anchorage | Small, fits standard D-rings |
Typical Use | Rebar, scaffolding, structural steel | Harnesses, lanyards, fixed points |
Profile | Bulky, robust | Compact, lightweight |
You should select the hook that matches the size and type of anchorage on your job site. The right fit ensures your equipment works as intended and keeps you safe during a fall.
Safety & Fall Protection
Safety is the top priority when choosing between rebar hook vs snap hook. Both types play a critical role in fall protection, but their safety features and risks differ. Rebar snap hooks excel in fall arrest system setups where you need to connect to large or irregular anchorage points.
Their robust construction and large gate opening reduce the risk of accidental disengagement during a fall.
Snap hooks must meet strict standards for gate strength and locking mechanisms. According to ANSI Z359.1-2007, snap hooks require a gate strength of 3,600 pounds in all directions to prevent accidental opening.
Incident reports show that snap hooks can fail if you apply side loading or defeat the locking gate. User education remains essential to prevent incompatible connections and ensure proper use.
Aspect | Snap Hooks | Rebar Hooks |
|---|---|---|
Locking Mechanism | Documented failures due to ease of defeating the locking gate. | N/A |
Side Loading Issues | Failures occur when loads are applied incorrectly, leading to disengagement. | N/A |
Standards Compliance | ANSI Z359.1-2007 requires stronger gates to reduce failure risk. | N/A |
Education and Awareness | Emphasizes the need for user education to prevent incompatible connections. | N/A |
Always inspect your hooks and lanyard before use. Confirm that the locking mechanism engages fully and that you connect to a compatible anchorage.
Ease of Use
You want your fall protection equipment to work smoothly, especially when you need to act quickly. Rebar snap hooks offer a large gate opening, which makes them easy to attach even when you wear gloves or work in tight spaces. This feature saves time and reduces frustration on busy job sites.
Snap hooks, with their compact size, allow for quick connections to standard D-rings and harnesses. You benefit from their lightweight design, which reduces fatigue during long shifts.
Rebar snap hooks: Best for oversized anchorage and fast connections in complex environments.
Snap hooks: Ideal for standard harnesses, lanyards, and equipment where space is limited.
Durability
Durability matters when you rely on your fall protection system every day. Both rebar hook vs snap hook options use high-quality materials to withstand tough job site conditions. Rebar hooks often feature high strength steel with a corrosion resistant finish and abrasion resistant webbing.
This combination ensures long-lasting performance, even in harsh environments. Snap hooks use yellow or silver zinc plating to protect against rust, which helps maintain their strength and reliability.
Hook Type | Corrosion Resistance | Material Wear Resistance |
|---|---|---|
Rebar Hook | High strength steel with corrosion resistant finish | Abrasion resistant webbing |
Snap Hook | Yellow/silver zinc plating protects against rust | Not specified in the evidence |
Tip: Regularly inspect your equipment for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any component that shows weakness to maintain your fall protection.
Applications
You must match your hook choice to your specific application. In construction, rebar snap hooks shine when you need to connect to large anchorage points like rebar assemblies or scaffolding.
These hooks work well with shock absorbing lanyards and fall arrest system setups, providing secure connections in dynamic environments. Snap hooks serve you best in situations where you connect to standard D-rings, harnesses, or fixed anchorage points.
You find them in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace industries, where compact size and quick operation matter.
Standard | Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|
ANSI Z359.1-2007 | Snap hooks must have a gate strength of 3,600 pounds in all directions | This standard aims to reduce the risk of incompatible connections. |
ANSI Z359.1-1992 | Snap hooks required to withstand a 5,000-pound tensile load | Misunderstandings about load application led to accidents. |
ANSI Z359.12-200X | Will provide detailed design requirements for connectors | Expected to enhance safety in fall protection systems. |
When you compare rebar hook vs snap hook, consider the type of anchorage, the fall protection system you use, and the specific requirements of your industry. The right choice keeps you safe, ensures compliance, and helps your equipment perform at its best.
Rebar Snap Hooks: Key Advantages
Large Gate Opening
You gain a clear advantage with rebar snap hooks because of their large gate opening. This feature allows you to connect quickly to oversized anchor points, such as scaffolding, rebar assemblies, or structural steel.
When you work at height, you often need to attach your lanyard to anchors that standard hooks cannot fit. The wide gate makes this process smooth and efficient, even if you wear gloves or work in tight spaces.
Industry standards have evolved to address the need for stronger, safer connections. The table below shows how requirements have changed to improve compatibility and safety:
Standard | Key Features | Compatibility Impact |
|---|---|---|
ANSI Z359.1-1992 | Required self-closing and self-locking gates, 5,000-pound tensile load | Assumed load application was misleading |
ANSI Z359.1-2007 | Revised requirements for gate strength and load application | Enhanced compatibility and safety in connections |
Tip: Always check that your lanyard and rebar snap hooks meet the latest safety standards before starting work.
Versatility
You benefit from the versatility of rebar snap hooks on diverse job sites. These hooks adapt to a wide range of anchorage points, making them suitable for many fall protection systems.
You can use them with horizontal lifelines, vertical lifelines, or directly with a lanyard. This flexibility means you do not need to carry multiple types of connectors for different tasks.
The fall protection community recognized the importance of hardware compatibility.
Manufacturers anticipated changes in industry requirements for stronger gates.
Some manufacturers resisted changes, leading to potential incompatibility.
You should always select hooks that match your specific application. When you choose rebar snap hooks, you ensure that your lanyard connects securely, no matter the size or shape of the anchor. This adaptability helps you stay safe and productive in changing work environments.
Pros and Cons
Rebar Hook
When you choose a rebar hook, you gain several advantages for demanding job sites. The large gate opening stands out as a key benefit, letting you connect quickly to oversized anchor points like scaffolding or rebar assemblies.
This feature saves time and reduces frustration, especially when you wear gloves or work in tight spaces. The robust construction ensures long-term durability, even in harsh environments. You can rely on these hooks for consistent performance in fall protection systems.
However, rebar hooks tend to be bulkier than snap hooks. You may find them less convenient when you need to connect to standard D-rings or smaller anchor points. Their size can add weight to your gear, which may affect comfort during long shifts.
Note: Always inspect your rebar hook before use to confirm the locking mechanism works properly and the hook shows no signs of wear.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Large gate opening for oversized anchors | Bulky compared to snap hooks |
Durable construction for tough jobs | Less suited for small anchor points |
Reliable in fall protection systems | Can add weight to your harness setup |
Snap Hook
Snap hooks offer a compact and versatile solution for many applications. You benefit from their lightweight design, which makes them easy to handle and ideal for connecting to standard D-rings or harnesses.
Many snap hooks feature a corrosion-resistant finish, so you can trust them to last in challenging environments. The Comfort Grip snaphook, for example, is engineered to withstand transverse loads up to 3,600 lbs. This design reduces the risk of connection failure during a fall, enhancing your safety.
You should note some limitations. Snap hooks must have a minimum tensile strength of 5,000 lbs and a locking mechanism sized to prevent disengagement. You cannot connect snap hooks directly to webbing, rope, or cable unless designed for that purpose.
Connecting snap hooks to other hooks or to a D-ring with another snap hook is not allowed.
The Comfort Grip snaphook uses a shear pin that breaks under sideways loading, improving flexibility and alignment.
Snap hooks excel in quick, secure connections but require careful attention to connection rules.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Lightweight and compact | Not for direct connection to webbing/rope |
Corrosion-resistant finish | Cannot connect to other hooks |
High tensile and transverse strength | Must follow strict connection guidelines |
Tip: Always follow manufacturer instructions to ensure your snap hook provides the best protection.
Choosing the Right Hook
Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the right hook for your job site can make a significant difference in your safety and efficiency. Follow these steps to ensure you choose the best option:
Assess Your Work Environment
Identify the type of anchorage points you encounter most often. If you work around large structures like scaffolding or rebar, a rebar hook may suit your needs. For standard D-rings or harness attachments, a snap hook often works best.Check Safety Standards
Review the safety requirements for your industry. Confirm that your chosen hook meets ANSI and OSHA standards. The right lanyard should always comply with these regulations.Evaluate Anchorage Requirements
Measure the size and shape of your anchor points. A rebar hook fits oversized or irregular anchors, while a snap hook connects easily to smaller, standard points.Consider Your Fall Protection System
Decide if you need a tie-back lanyard or a system designed for fall restraint. Match your hook choice to the lanyard and system you use.Inspect for Compatibility
Ensure your hook, lanyard, and anchorage work together. Test the locking mechanism before each use.
Tip: Always inspect your equipment before starting work. Replace any worn or damaged parts immediately.
Quick Checklist
Use this checklist to confirm you have selected the right hook:
Criteria | Rebar Hook | Snap Hook |
|---|---|---|
Oversized anchor points | ✅ | |
Standard D-rings | ✅ | |
Meets safety standards | ✅ | ✅ |
Right lanyard attached | ✅ | ✅ |
Fall restraint system | ✅ | ✅ |
Tie-back lanyard use | ✅ |
If you check more boxes in one column, that hook is likely the best fit for your application.
Conclusion
You now understand the key differences between rebar hooks and snap hooks. Rebar hooks work best for oversized anchor points and heavy-duty fall protection. Snap hooks fit standard D-rings and offer a compact, versatile option.
Choose rebar hooks for large, irregular anchors.
Choose snap hooks for everyday harness and tool connections.
Always follow safety standards and consult a professional if you have questions. Make your choice with confidence and keep your workplace safe.
FAQ
What is the main hazard when using the wrong hook for fall protection?
You face a serious hazard if you use the wrong hook. An improper connection can fail during a fall. This risk increases when you do not match the hook to the anchorage point. Always check compatibility before use.
Why is insufficient anchorage strength a concern with rebar and snap hooks?
Insufficient anchorage strength can lead to equipment failure. You must ensure the anchorage point supports the required load. Both rebar hooks and snap hooks need strong, secure anchors to prevent accidents.
How does a self-retracting lanyard compare to an energy-absorbing lanyard for hook connections?
A self-retracting lanyard limits fall distance and works well with both hook types. An energy-absorbing lanyard reduces impact force. You should choose the right lanyard based on your connection needs and job site conditions.
What is the leading cause of fatalities in fall protection?
The leading cause of fatalities in fall protection is improper use or failure of equipment. You must inspect your hooks and connections regularly. Always follow safety guidelines to reduce this risk.
Can the wrong hook choice contribute to a fatality?
Yes, using the wrong hook can result in a fatality. If the connection fails during a fall, the consequences can be severe. Always select the correct hook for your application and inspect it before use.


