You protect your team and equipment when you prioritize Wire Rope Inspection. Industry standards recommend daily visual checks before each shift and more thorough inspections on a weekly or monthly basis, depending on the workload and environment.
The table below shows how OSHA and ASME outline inspection schedules:
Source | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|
OSHA | Monthly inspections required; annual inspections by a qualified person |
ASME | Daily visual inspections; more thorough inspections based on conditions (weekly/monthly) |
Neglecting inspections can lead to costly failures and safety hazards. High-quality options like Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope help you maintain reliability and peace of mind.
Key Takeaways
Conduct daily visual inspections of wire ropes before each use to catch potential issues early.
Follow OSHA and ASME guidelines for regular inspections to maintain safety and compliance.
Document all inspections thoroughly to prepare for audits and ensure accountability.
Use proper storage and handling techniques to extend the lifespan of wire ropes and prevent damage.
Replace wire ropes immediately if you find broken wires or significant wear to avoid accidents.
Importance of Wire Rope Inspection

Safety and Compliance
You protect your workplace when you conduct wire rope inspections regularly. The purpose of wire rope inspections is to ensure maximum safety for your team and equipment.
Regulatory bodies such as OSHA and ASME require strict adherence to inspection schedules. If you fail to follow these standards, your company may face serious penalties.
Type of Penalty | Description |
|---|---|
Fines | Monetary penalties for violations. |
Legal fees | Costs incurred for legal representation. |
Injunctive relief | Court orders to comply with regulations. |
Criminal charges | Potential criminal prosecution. |
Reputational damage | Harm to business reputation. |
Increased workers’ compensation rates | Higher insurance costs due to non-compliance. |
You avoid these risks by making wire rope inspection part of your daily routine. This commitment not only keeps your operations compliant but also builds trust with clients and employees.
Preventing Failures
Wire rope inspections help you identify problems before they become hazards. You reduce the chance of accidents and costly downtime when you spot issues early. Common safety incidents in industrial settings include:
Corrosion, often hidden and caused by poor lubrication, can lead to dangerous failures.
Fatigue, which results from repetitive bending, causes cracks and wire breaks.
Abrasion, due to irregular contact with hoist sheaves or external objects, leads to significant damage.
If you neglect wire rope inspection, you risk catastrophic injuries and fatalities. The sudden release of tension can create a whip-like effect, endangering everyone nearby. You also face financial consequences, such as medical expenses, legal fees, and equipment repairs.
Operational downtime can disrupt your business and delay projects.
You maintain maximum safety and reliability when you conduct wire rope inspections as part of your routine. This proactive approach protects your team, equipment, and reputation.
Wire Rope Types and Strength
Classifications and Ratings
You encounter several wire rope types in industrial settings. Galvanized wire ropes offer strong corrosion resistance, making them ideal for outdoor or marine environments. Stainless steel wire ropes perform best in areas exposed to moisture.
Each type has a specific wire rope classification that determines its suitability for different tasks. You must pay close attention to wire rope strength, which includes minimum breaking strength and working load limit (WLL). These ratings help you avoid overloading and prevent dangerous failures.
Characteristic | Impact on Safety and Performance |
|---|---|
Strength | Determines the maximum load the rope can safely handle. |
Flexibility | Affects the rope’s ability to bend without breaking. |
Abrasion resistance | Reduces wear and tear, prolonging rope life. |
Crushing resistance | Prevents damage under heavy loads. |
Fatigue resistance | Ensures durability under repeated loading cycles. |
Corrosion resistance | Protects against environmental damage. |
Rotation resistance | Maintains stability during lifting operations. |
You select the right wire rope by matching its classification and ratings to your application. This approach ensures safety and extends the lifespan of your equipment.
Mill Certificates and Standards
You verify wire rope strength and quality by reviewing mill certificates and inspection reports. These documents confirm that your steel wire rope meets industry standards and specifications.
Mill certificates include manufacturer details, product specifications, chemical composition, and mechanical property testing. You also find results from hardness, impact, and non-destructive tests. Quality control approvals guarantee that each wire rope passes strict inspections.
Mill test certificates (MTC 3.1 or 3.2)
Dimensional inspection reports
Mechanical property reports
Surface inspection results
Corrosion resistance test data
Heat number and production traceability information
You maintain compliance and safety by keeping these records for every steel wire rope you use.
Powerful Machinery Steel Wire Rope Features
You benefit from advanced features when you choose Powerful Machinery steel wire rope. Modern manufacturing processes produce lighter, stronger, and more flexible ropes. Improved coatings and treatments extend service life, even in extreme conditions.
Automation increases production efficiency and consistency. Innovations in structural design enhance load-bearing capabilities and safety. Sustainable techniques and recyclable materials support environmental responsibility.
Tip: Powerful Machinery steel wire rope offers non-rotating designs, high tensile strength, and superior resistance to abrasion and corrosion. You achieve reliable performance in construction, marine, and transportation applications.
Wire Rope Inspection Standards
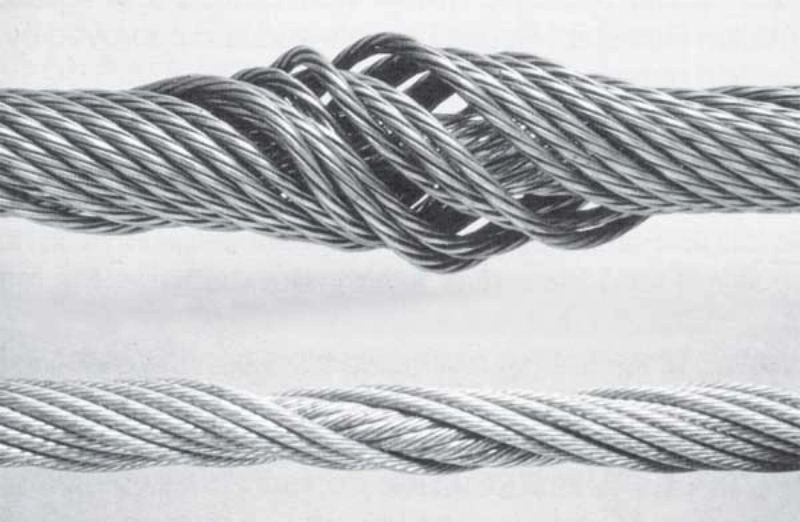
OSHA and ASME Guidelines
You must follow strict inspection standards to keep your wire ropes safe and compliant. OSHA and ASME set clear requirements for inspection frequency and documentation. The table below outlines their recommendations:
Inspection Type | Frequency | Documentation Requirement |
|---|---|---|
Frequent Inspection | Daily or Before Use | Not required |
Periodic Inspection | At least every 12 months | Required for below-the-hook devices; not required for individual slings |
Continuous Service Check | Daily during operation; Weekly | Not specified |
Thorough Inspection | Monthly for devices not used for a month | Required for documented inspection of condition |
You designate a qualified person to inspect slings and attachments daily for damage or defects. You schedule periodic inspections at intervals no greater than 12 months.
For normal service, you inspect yearly. For severe service, you inspect monthly or quarterly. You replace ropes if wear on individual wires exceeds one-third of the diameter.
Tip: Consistent documentation helps you meet compliance requirements and prepares you for safety audits.
ISO 4309 and Global Standards
You encounter global standards like ISO 4309 and FEM when inspecting wire ropes. These standards classify wire rope hoists based on duty cycles and lifespan.
ISO and FEM use different methods, but both aim to ensure a minimum theoretical lifespan for hoists under specified conditions. You benefit from these standards because they help you select the right wire rope for your application and maintain safe operations.
ISO 4309 sets guidelines for inspection, discard criteria, and maintenance.
FEM standards focus on categorizing hoists by usage and expected service life.
Both standards promote consistent safety practices worldwide.
Powerful Machinery Certification
You gain confidence in your equipment when you choose Powerful Machinery steel wire rope. Powerful Machinery products hold certifications such as ISO 2408, EN 12385, and DIN 3060.
These standards establish requirements for tensile strength, construction, and testing. Third-party certifications from organizations like TÜV and SGS provide impartial endorsement of compliance with quality standards.
ISO 2408, EN 12385, and DIN 3060 ensure wire rope quality and reliability.
TÜV and SGS certifications verify adherence to international safety standards.
Powerful Machinery wire ropes meet rigorous testing and inspection protocols.
You maintain safety and compliance by selecting certified wire ropes for your lifting and rigging needs.
Wire Rope Inspections: Frequency and Documentation
Daily and Scheduled Checks
You must establish a routine for wire rope inspections to maintain safety and compliance. Start each shift with a daily inspection. A competent person should check all running ropes and slings before use.
Look for visible hazards such as kinking, corrosion, or broken wires. This habit helps you catch problems early and prevent accidents.
Set up periodical inspections based on your work environment. For most operations, schedule a thorough inspection at least every 12 months. If you work in severe conditions or use your equipment frequently, increase the frequency to monthly or quarterly.
Always document these checks, noting the date, inspector’s name, and any findings.
Conduct daily visual checks before each use.
Schedule periodical inspections every 12 months, or more often in harsh conditions.
Record each inspection for future reference.
Event-Driven Inspections
Certain events require immediate wire rope inspections outside your regular schedule. If you notice unusual wear or damage, act quickly. The table below lists common triggers for unscheduled inspections:
Condition | Description |
|---|---|
Abrasion | Damage from contact with rough surfaces or worn parts. |
Corrosion | Rust or internal degradation often needs immediate lubrication. |
Wire Breaks | Multiple broken wires signal the need for replacement. |
Crushing | Deformation from improper installation or spooling. |
Shock Loading | Sudden tension release causes irreversible damage. |
You should inspect your wire rope after any of these events. Prompt action helps you avoid unexpected failures and keeps your team safe.
Record-Keeping Best Practices
Accurate records support your compliance with OSHA and ASME standards. For each wire rope inspection, include the rope identifier, inspection date, and the inspector’s name. Keep these records organized and accessible for audits or safety reviews.
Document every periodical inspection as required by ASME B30.9.
Maintain comprehensive records to meet OSHA requirements.
Store records in a central location for easy access during audits.
Tip: Good documentation not only proves compliance but also helps you track the condition of your equipment over time.
Wire Rope Inspection Tools and Methods
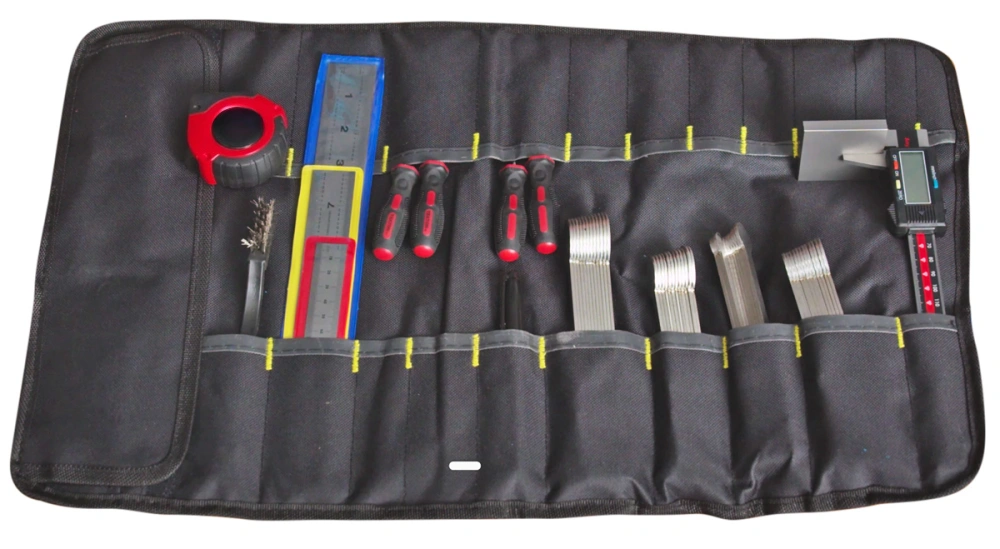

Visual and Measurement Tools
You rely on the right tools to perform a thorough visual wire rope inspection. Start with a strong flashlight and a magnifying glass to check for surface wear, corrosion, and broken wires. Use calipers or micrometers to measure rope diameter and detect any reduction that signals internal damage.
Non-destructive testing devices, such as flaw detectors, help you assess the rope’s condition without causing harm. These tools measure loss of metallic area and identify localized flaws like broken wires and corrosion.
Electromagnetic detection technology and ultrasonic testing also play a role. They allow you to find hidden defects by analyzing changes in magnetic fields or ultrasonic wave reflections.
Flashlight and magnifying glass for surface checks
Calipers or micrometers for diameter measurement
Flaw detectors for internal assessment
Electromagnetic and ultrasonic testers for advanced analysis
Tip: Consistent use of these tools during visual wire rope inspection helps you catch problems early and maintain safety.
Cloth Rag and Diameter Checks
You can use a simple cloth rag to detect broken wires during inspections. Pull the rag slowly along the length of the wire rope. If the rag snags or catches, you may have found a protruding broken wire. This method helps you identify external damage that might not be visible at first glance.
Always follow up with a diameter check using a caliper. Compare your measurements to the rope’s original specifications. A significant reduction in diameter often indicates internal wear or core failure.
Move the rag slowly along the rope to feel for snags
Use a caliper to measure rope diameter at several points
Record any changes or irregularities for future reference
Advanced Inspection Systems
You can enhance accuracy and efficiency with advanced inspection systems. AI and computer vision now detect critical wear indicators with high precision. These systems create digital inspection records, which improve reliability and streamline audits.
Machine vision inspection technology uses high-definition cameras to spot surface defects like rust and abrasion. Magnetic flux leakage and acoustic emission testing provide real-time alerts for internal breaks and corrosion.
Some facilities use automatic wire rope cleaning devices and oil immersion systems to maintain cleanliness and lubrication, ensuring accurate inspections and longer service life.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Automatic Wire Rope Cleaning Device | Cleans wire rope efficiently for better inspection accuracy |
Wire Rope Nondestructive Testing | Uses electromagnetic detection for real-time integrity assessment |
Wire Rope Oil Immersion Device | Applies maintenance oil automatically to extend the rope’s lifespan |
Note: Advanced systems reduce downtime and help you maintain safety in critical environments.
Wire Rope Inspection Procedure
Visual Checks for Damage
You begin the wire rope inspection process by performing a thorough visual check for damage. This step helps you identify warning signs before they become serious hazards. Start by looking for distortion, such as wave patterns, bird-caging, or kinking.
These forms of deformation often signal underlying problems with the rope’s structure. Use a cloth rag to test for broken wires. Pull the rag slowly along the rope’s length. If the rag snags, you have likely found a protruding broken wire.
Inspect the rope for abrasion, corrosion, and pitting. These types of wear reduce the rope’s strength and reliability. Check for proper lubrication, as dry or poorly lubricated ropes are more prone to damage. Pay close attention to areas that bend or pass over pulleys, since these spots experience the most wear.
Tip: Always look for warning signs like rust, broken wires, or unusual bends. Early detection helps you prevent accidents and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Measuring Diameter and Wear
You must measure the diameter of your steel wire ropes to assess wear and ensure compliance with safety standards. Use a certified parallel-jawed caliper or a digital gauge for accurate results. Position the caliper jaws at a right angle to the rope’s axis, making sure they touch the outermost wires.
Close the jaws gently until they contact the rope without compressing it. Read the diameter from the caliper or digital display.
Measure the diameter at three different points along the rope and calculate the average. This method helps you detect any significant size reduction, which is a clear warning sign of internal wear or core failure. According to ASTM and API standards, wire ropes are manufactured slightly larger than the nominal diameter.
The nominal diameter represents the minimum allowed size. If your rope measures below this limit, you must consider replacement.
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Select a caliper | Use a certified parallel-jawed caliper or digital gauge |
Position correctly | Place the jaws at a right angle to the rope’s axis |
Close gently | Avoid compressing the rope |
Take measurements | Record diameter at three points |
Calculate average | Determine if reduction exceeds safe limits |
Note: Regular diameter checks help you track wear and maintain safe operations. If you notice a reduction beyond acceptable limits, replace the rope immediately.
Inspecting Attachments and Fittings
You must inspect all attachments and fittings as part of the wire rope inspection process. Lay the sling on a flat surface to ensure visibility. Clean the sling with a rag or a wire brush to remove dirt and grease. This step allows you to see wear and damage more clearly.
Examine the entire sling, focusing on areas prone to wear. Pay special attention to fittings and end attachments, as these components often show early warning signs of damage. Compare any found damage against the service removal criteria set by OSHA.
Label inspected wire rope slings and maintain detailed records, including inspection dates and conditions. Dispose of rejected slings immediately to prevent accidental use.
Ensure all parts are visible and accessible
Clean the sling for better inspection accuracy
Examine the entire sling, focusing on wear-prone areas
Inspect fittings and attachments thoroughly
Compare damage against removal criteria
Label and record inspected slings
Store slings safely, away from harmful conditions
While visual inspections are common, you must be thorough. Neither OSHA nor ASME prescribes a fixed inspection process, so you should establish a procedure based on your specific requirements and usage. Consistent and careful inspections help you catch warning signs early and maintain a safe work environment.
Callout: Always dispose of slings that fail inspection. Keeping damaged equipment in service increases the risk of accidents and injuries.
If you want to know how to inspect steel wire ropes effectively, follow these steps for each inspection process. You protect your team and equipment by identifying wear and damage before they lead to failure.
Broken Wires and Replacement Criteria
Identifying Broken and Damaged Wires
You must recognize the early signs of broken wires to prevent wire rope failure and ensure safe operations. When you inspect steel wire ropes, look for visible damage and subtle changes in rope behavior. Common indicators include:
Kinks and twists that disrupt the rope’s ability to bear a uniform load.
Unnatural bends or hard kinks signal significant damage.
Loss of flexibility, which makes the rope stiff and difficult to handle.
Bulging or excessive elongation is often caused by internal damage or overload.
Lack of lubrication leaves the rope dry and more likely to break.
Abrasion damage from rough surfaces, which reduces strength.
Internal or external damage to the core or outer strands.
Excessive stretching, which shows the rope has lost strength over time.
You should also check for broken wires along the rope’s length. If you find clusters of broken wires or notice a single broken wire near the end connection, you must consider removal from service.
Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope features high tensile strength and advanced coatings, which help resist abrasion and reduce the risk of fracture. However, even the most durable ropes require regular inspection to catch broken wires before they lead to fatigue fracture or catastrophic failure.
Tip: Always inspect the rope after any shock loading or unusual event. Early detection of broken wires helps you avoid costly repairs and maintain safety.
Replacement Criteria for Steel Wire Rope
You need to follow strict replacement criteria to keep your lifting operations safe. Industry standards set clear thresholds for broken wires and other damage types. The table below summarizes when you must replace the rope based on wire breaks:
Condition | Threshold for Replacement |
|---|---|
Running Ropes | Six randomly distributed broken wires in one layer |
Three broken wires in a single strand in one lay | |
Standing Ropes | More than two broken wires in one lay |
A single broken wire near the end connection | |
Localized clusters of broken wires indicate deeper fatigue, prompting retirement. |
You must remove the rope from service if you reach any of these thresholds. If you see signs of fatigue fracture, such as multiple broken wires in a concentrated area, replace the rope immediately. You should also retire the rope if you notice excessive abrasion, loss of diameter, or any fracture in the core or outer strands.
Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope meets international standards for durability and safety, but you must still follow these guidelines to prevent wire rope failure.
Note: Never attempt to repair rope with broken wires. Replacement is the only safe option when you reach the removal from service criteria.
Special Cases: Rotation-Resistant Ropes
You must pay special attention to rotation-resistant ropes, as their design makes them more susceptible to hidden internal damage. These ropes resist twisting and provide better load control, but their internal structure can mask broken wires and fatigue fractures.
You need to inspect rotation-resistant ropes more frequently, especially if you use them for repetitive lifts or high-duty cycles.
The replacement criteria for rotation-resistant ropes differ from standard ropes due to their unique design and higher risk of internal damage.
You must monitor duty cycles and repetitive lifts closely, as these factors increase the likelihood of internal fracture.
Always check for signs of broken wires inside the rope, not just on the surface. Use advanced inspection tools if available.
If you detect any broken wires or suspect internal damage, remove the rope from service and replace it immediately.
Powerful Machinery’s non-rotating steel wire rope offers superior resistance to twisting and meets strict international standards, but you must still follow the recommended replacement criteria for rotation-resistant ropes.
Callout: Rotation-resistant ropes require extra vigilance. Regular inspections and prompt removal from service help you prevent accidents and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Wire Rope Maintenance Best Practices
Storage and Handling
You protect your investment when you follow proper wire rope storage and handling procedures. Store wire ropes in a dry, temperate environment to prevent wire rope corrosion and deterioration. Always ventilate packaging to avoid moisture build-up.
Cover reels with waterproof materials if you store them outside. Inspect stored wire ropes every six months for signs of damage. Maintain ambient temperatures below 50° C to optimize service life. Keep wire ropes in an acid-free environment to prevent corrosion and degradation.
Apply a high-quality lubricant to maintain flexibility and shield against wire rope corrosion.
Store wire ropes away from direct sunlight and harsh chemicals.
Handle wire ropes gently to avoid kinks and crushing.
Use protective gloves and proper lifting equipment during handling.
Tip: Regular inspections and careful storage extend the lifespan of your wire ropes.
Cleaning and Lubrication
You maintain wire rope integrity by cleaning and lubricating regularly. Cleaning removes dirt, grit, and old lubricants that trap moisture and cause damage. Scraping, steaming, or high-pressure washing can remove contaminants. Use a wire brush for rust removal.
Always clean before lubrication to prevent pushing contaminants deeper into the rope. Choose the right lubrication method for your operation. Manual lubrication covers outer wires, while semi-automatic methods use drip or spray.
Automatic lubrication provides the best penetration and protection against wire rope corrosion. Routine wire rope lubrication aligns with operational demands and keeps your ropes flexible.
Pre-cleaning allows new lubricants to reach the core.
Ignoring cleaning risks, worker safety, and equipment integrity.
Extending Lifespan in Harsh Environments
You face extra challenges in mining, marine, and other harsh environments. Conduct regular inspections to detect wear and damage early. Use proper lubrication to reduce friction and prevent wire rope corrosion. Handle and use wire ropes correctly to avoid premature wear.
Protect wire ropes from UV exposure and corrosive elements. Store wire ropes away from direct sunlight. Use galvanized or stainless steel wire ropes in corrosive settings. Clean wire ropes regularly and replace them when you see signs of damage.
Callout: Timely replacement and routine maintenance help you avoid costly failures.
Powerful Machinery Maintenance Tips
You maximize performance and safety by following Powerful Machinery’s maintenance recommendations.
Maintenance Tip | Description |
|---|---|
Inspection | Check for wire breaks and measure groove diameters regularly. |
Cleaning | Remove contaminants thoroughly to prevent wear. |
Lubrication | Apply suitable lubricants to reduce internal wear and protect against corrosion. |
Safe Handling | Avoid overload and ensure proper wire rope storage to prevent damage. |
You ensure reliable operation and extend the lifespan of your wire ropes when you follow these wire rope maintenance best practices.
Prolonging Wire Rope Lifespan
Marine and Industrial Applications
You face unique challenges when you use wire ropes in marine and industrial environments. These settings expose ropes to heavy loads, harsh weather, and abrasive materials. To maximize lifespan, you must understand the main factors that affect performance:
Working Environment: Handling rough or dirty cargo increases wear.
Operator Handling Techniques: Skilled operation reduces stress and prevents early failure.
Cleaning and Greasing Frequency: Regular maintenance keeps corrosion and friction under control.
Sheave Maintenance: Well-maintained sheaves prevent uneven wear on the rope.
Rope Design and Load: High-quality materials and tailored constructions improve durability.
Vessel Type and Mooring Arrangement: The way you use and arrange ropes impacts their longevity.
Position and Usage: Some lines wear out faster due to frequent use or exposure.
Ports and Trading Patterns: Different environments and routes can accelerate damage.
Inspection Procedures: Routine checks help you catch problems early.
Storage and Handling Practices: Proper storage keeps ropes safe from unnecessary harm.
Tip: You extend the life of your wire ropes by combining skilled operation, regular maintenance, and proper storage.
Preventing Corrosion and Abrasion
You protect your wire ropes from corrosion and abrasion by using proven methods. The right approach depends on your environment and application. The table below summarizes effective strategies:
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Protective Coatings | Apply galvanization or polymer coatings to block rust and moisture. |
Lubrication | Use lubricants to create a barrier against corrosive agents. |
Petroleum-based | Choose for cost-effective protection in moderate conditions. |
Synthetic blends | Use for resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. |
Specialty formulations | Select for environments needing extra corrosion inhibitors. |
You should apply protective coatings and lubricants regularly. These steps shield the rope from water, salt, and chemicals. Choose the right lubricant for your conditions—petroleum-based for general use, synthetic blends for tough environments, and specialty products for extreme cases.
Callout: Consistent maintenance and the right protective measures help you avoid costly replacements and keep your operations running smoothly.
Conclusion
You ensure safety and reliability when you follow a routine of wire rope inspection, maintenance, and timely replacement. Choose certified products like Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope to meet industry standards and boost performance.
Stay proactive with regular checks and detailed records. By making inspection and care a priority, you protect your team, equipment, and reputation.
FAQ
How often should you inspect wire ropes?
You should inspect wire ropes daily before use and schedule thorough inspections monthly or annually, depending on your work environment. Frequent checks help you catch damage early and maintain compliance with safety standards.
What signs indicate you need to replace a wire rope?
Look for broken wires, reduced diameter, severe corrosion, kinks, or loss of flexibility. If you find six broken wires in one lay or three in a single strand, you must replace the rope immediately.
Can you use Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope outdoors?
Yes. Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope resists corrosion and abrasion. You can use it in outdoor, marine, and industrial environments. Its high-grade steel and advanced coatings ensure durability in harsh conditions.
What is the advantage of a non-rotating wire rope?
A non-rotating wire rope prevents twisting and kinking during lifting operations. You gain better load stability and reduce the risk of accidents. This design extends the rope’s lifespan and improves safety.


