Selecting the right anchor chain material is crucial for your vessel’s safety and performance. Steel dominates the marine industry for anchor chains because it offers high tensile strength and resists corrosion, making it ideal for any anchoring system.
When setting anchor, you must also consider grade, size, calibration, and anchor rode length. Powerful Machinery provides certified anchor chains trusted by marine professionals worldwide. Choosing the right materials ensures reliable performance in demanding conditions.
Key Takeaways
Choose steel or galvanized materials for strong, corrosion-resistant anchor chains. This ensures safety and durability in marine environments.
Match the anchor chain grade to your vessel’s size and weight. Higher grades provide better strength and reliability under heavy loads.
Calculate the correct anchor chain length using a 7:1 scope ratio for secure anchoring. This helps maintain stability in changing water conditions.
Regularly inspect your anchor chain for rust and wear. Maintenance extends the life of your equipment and ensures safe anchoring.
Consult with experts like Powerful Machinery for certified anchor chains. Their guidance helps you select the best materials for your specific needs.
Key Factors in Anchor Chain Material Selection

Choosing the right anchor chain material for your vessel requires careful consideration of several factors. You must evaluate the type of material, its corrosion resistance, strength, cost, and suitability for your specific application.
Powerful Machinery offers a wide range of certified anchor chains designed to meet the demands of marine professionals. You can rely on their expertise to guide you through the selection process.
Material Types and Corrosion Resistance
You will encounter several anchor chain material options in the marine industry. Each type performs differently in terms of corrosion resistance and durability. The table below summarizes the most common choices:
Type of Chain | Material Used | Corrosion Resistance Effect |
|---|---|---|
High-tensile marine-grade alloy steel | Alloy steel | High strength and corrosion resistance |
Galvanized chains | Hot-dip coated steel | Enhanced corrosion protection in saltwater |
Black chains | Untreated steel | Lower corrosion resistance, best for freshwater or cost-sensitive applications |
Galvanized anchor chains provide enhanced protection in saltwater due to their zinc coating. However, you should note that the coating can wear off after one season, which reduces the diameter of the links and affects the holding force. The lifetime of hot-dip galvanized steel varies.
In brackish waters, the coating lasts two to three years for partial immersion and over five years for full immersion. Galvanized steel performs well under normal conditions, but the protective layer is prone to damage, which can lead to oxidation and rust.
Tip: Regular inspection and maintenance help extend the life of your anchor chain material, especially in harsh marine environments.
Strength, Durability, and Cost
You must match the strength of your anchor chain to the size and weight of your vessel. The grade and material type determine the minimum breaking strength. The table below compares the tensile strength values for different anchor chain materials:
Chain Grade | Material Type | Minimum Breaking Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
G30 | Carbon Steel | 300 |
G40 | Carbon Steel | 400 |
G43 | Carbon Steel | 430 |
G70 | Heat-Treated Steel | 700 |
G3 | Stainless | Lower than G4 |
G4 | Stainless | Higher than G3 |
G6 | Stainless | Supreme quality |
Grade 30 | Galvanized | Lower than Grade 40 |
Grade 40 | Galvanized | Standard |
Grade 70 | Galvanized | Higher than Grade 40 |
Cost is another important factor. You need to balance your budget with the required performance. The following table shows the average price range for popular anchor chain types:
Type of Chain | Average Price Range (per foot) |
|---|---|
1/4 inch (6 mm) Galvanized Chain | $5 – $10 |
3/8 inch (10 mm) Galvanized Chain | $7 – $15 |
5/16 inch (8 mm) High-Test Chain | $6 – $12 |
3/8 inch (10 mm) High-Test Chain | $8 – $20 |
1/2 inch (13 mm) High-Test Chain | $10 – $25 |
3/4 inch (19 mm) Stud Link Chain | $20 – $40 |

You should select an anchor chain material that offers the right balance of strength, durability, and cost for your vessel and operating environment.
Common Use Cases and Recommendations
Different vessels require specific anchor chain materials based on their size, purpose, and environment. The table below provides recommendations for common use cases:
Material | Characteristics | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
Steel | Exceptional strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and shock resistance | Commercial ships, military vessels |
Titanium | Excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | Military ships, submarines, cruisers |
Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, suitable for freshwater environments | Small recreational boats, dinghies |
Plastic/Synthetic | Lightweight, buoyant, soft, corrosion-resistant | Small boats, kayaks, recreational watercraft |
You must avoid common mistakes when selecting anchor chain material. Mismatching your chain and windlass gypsy can cause failure. Always ensure the chain matches the windlass gypsy exactly.
Neglecting to use a snubber or bridle puts excessive stress on the windlass and hardware. Using undersized or unsecured shackles creates weak points and increases the risk of failure.
Powerful Machinery provides anchor chains in various grades, sizes, and calibrations. Their products meet international standards and suit a wide range of marine applications. You can consult their technical team for guidance on selecting the best anchor chain material for your vessel.
Note: Always verify the compatibility of your anchor chain with your windlass and anchoring system before installation.
Comparing Galvanized and Stainless Steel Anchor Chains
Galvanized Anchor Chain Features
Galvanized anchor chains remain a popular choice for many boaters. You benefit from their cost-effectiveness and reliable strength. The zinc coating protects the chain from rust, but this layer can wear away quickly, especially in harsh marine environments.
You may notice rust and discoloration on your hull and deck after a season of use. Regular inspection and maintenance help extend the lifespan of your anchor chain. Users often report visible degradation after six months of full-time use, so you should feed out longer minimums to keep the chain clean.
Lower-quality chains may require more frequent replacement.
Feature | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
High Strength | Ensures stability and reliability under heavy loads. |
Corrosion Resistance | Prevents rusting, enhancing durability in marine conditions. |
Versatile Design | Adaptable to various applications, meeting specific needs. |
Cost-Effectiveness | Provides long-term value due to durability and longevity. |
Galvanized chains typically last 5-10 years under normal conditions. You must inspect your anchor chain regularly to maintain safety and performance.
Stainless Steel Anchor Chain Features
Stainless steel anchor chains offer superior corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater. You will find that chains made from AISI 316L are nearly rust-free and have a smooth finish. For extreme conditions, duplex or super duplex stainless steel provides enhanced heat and corrosion resistance.
Higher grades, such as 318L in Grades 50 and 60, deliver double the strength of standard 316 chain. However, stainless steel anchor chains cost three to four times more than galvanized options. Some alloys may have poor corrosion resistance in warm water, so you must choose the right grade for your environment.
Stainless steel anchor chains last 15-20 years, making them a long-term investment.
You need larger chain sizes for equivalent strength compared to galvanized chains.
Stainless steel requires less maintenance and maintains its appearance over time.
Choosing the Right Anchor Chain Material for Your Needs
You should consider several factors when selecting an anchor chain for your vessel. Vessel size and weight determine the required chain diameter and length. Marine conditions influence your choice; stainless steel suits corrosive saltwater environments, while galvanized steel offers strength and affordability.
Chain grade affects load-bearing capacity. Your budget plays a role, as stainless steel anchor chains cost more but provide better long-term performance. Regular maintenance is essential for both types.
Chain Type | Lifespan |
|---|---|
Galvanized Chains | 5-10 years |
Stainless Steel Chains | 15-20 years |
Hot-dip galvanized steel anchor chains remain the most popular due to their cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel anchor chains appeal to those who value rust resistance and aesthetics. You must match your anchor chain to your vessel’s specifications and operating environment for optimal safety.
Selecting Chain Grade, Size, and Calibration
Understanding Anchor Chain Grades
You must select the right anchor chain grade to ensure safety and performance for your vessel. Grades indicate the strength and durability of the chain. The table below summarizes the most common grades and their applications:
Chain Grade | Description | Strength Comparison | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Grade 30 | Common and affordable option for small to mid-sized boats. | Baseline strength | General use in typical conditions. |
Grade 43 | High Test chain, 50% stronger than Grade 30. | 50% more than G30 | Suitable for applications requiring reduced weight without sacrificing strength. |
Grade 70 | Transport chain, very strong, often used in industrial settings. | Overkill for recreational use | Best for lashing heavy equipment. |
Industry standards such as OSHA 1910.184 and ASME B30.9 regulate anchor chain grades. These standards ensure that your anchor chain meets strict safety and testing requirements.
Choosing Size and Calibration
You need to match the anchor chain size and calibration to your vessel’s displacement and anchor size. Calibrated chains fit precisely with the windlass gypsy, preventing slippage and damage. Proper calibration guarantees smooth operation and extends the life of your anchoring equipment.
Follow these steps to select the correct chain size:
Calculate your vessel’s displacement.
Use a chain size multiplier, typically between 1/8 and 1/6 of the vessel’s displacement.
Multiply the displacement by the multiplier to determine the minimum anchor chain diameter.
The table below shows typical diameters for different vessel sizes:
Diameter | Suitable For |
|---|---|
48mm | Smaller vessels or recreational boats |
50mm | Medium-sized vessels with moderate needs |
73mm | Medium to large vessels with higher demands |
81mm | Larger vessels like cargo ships and tankers |
87mm | Very large vessels like oil tankers |
90mm | Largest vessels such as supertankers |
Note: Using improperly sized or calibrated anchor chains can cause windlass problems, increased wear, and safety hazards.
Practical Selection Tips
You should always consider practical advice from marine safety organizations when choosing anchor chain specifications:
Determine the right length of chain for safe anchoring using a scope ratio. A 7:1 scope is recommended for overnight anchoring or rough conditions.
For calm conditions, a 4:1 scope may be sufficient.
Larger boats need one foot of chain for every foot of boat length. Smaller boats should have at least 5 to 10 feet of chain.
Calculate the correct scope before deploying your anchor and consider environmental factors such as seabed type and current strength.
Use the appropriate anchor for your conditions and secure the anchor line to prevent drifting.
Adjust your scope in crowded anchorages to reduce collision risk.
You must ensure that every component, including splices, shackles, and connectors, matches the strength of your anchor chain. Ignoring the weakest link can lead to anchor failure.
Calibration is essential for compatibility with your windlass and anchoring system. Adhering to standards like DIN766 and ISO4565 ensures precise link dimensions and reliable performance.
Determining Anchor Chain Length
Factors Affecting Length
You need to consider several important factors when deciding how much anchor chain your vessel requires. The right length ensures your anchor holds securely and keeps your boat safe in changing conditions. The following table outlines the main factors that influence your decision:
Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Vessel Size and Weight | Larger and heavier vessels require thicker and stronger chains for sufficient holding power. |
Anchor Type and Weight | Different anchors have varying holding capacities; matching anchor type with chain size is crucial. |
Water Depth | A general rule is a 5:1 scope ratio; chain length should be five times the water depth. |
Holding Requirements | Weather conditions, currents, and seabed type affect the required chain size for secure mooring. |
Regulatory Guidelines | Compliance with maritime regulations may dictate specific chain size requirements. |
You should also pay attention to these additional points:
Water depth and tides change during the day. Calculate your chain length based on the highest expected water level.
Seabed type matters. Sand, mud, or rocky bottoms may require different chain lengths for proper anchor holding.
Strong wind or current means you need a longer chain to keep your anchor secure.
Tip: Always check local regulations and weather forecasts before anchoring to ensure you meet safety standards.
Calculating the Ideal Anchor Chain Length
You can use several methods to calculate the best anchor chain length for your vessel. The most common approach is to use a scope ratio, which is the ratio of the length of chain paid out to the depth of the water.
The BoatUS Foundation recommends a 7:1 scope for most situations. For every foot of water depth, let out seven feet of anchor chain.
In calm conditions, a 5:1 scope may be enough, but 7:1 gives you extra security in rough weather.
For mid-size to large sailboats (30 to 50 feet) in high winds, use this formula: Chain length = 50 feet + 2 times the water depth (in feet).
You can also use this formula for precise calculation:
Anchor Line Length = Scope × (Water Depth + Bow Height)
This formula helps you account for both the water depth and the height of your bow above the waterline.
Example: If your bow is 4 feet above the water and you anchor in 10 feet of water, with a 7:1 scope, you need (10 + 4) × 7 = 98 feet of chain.
Note: Always round up your chain length for added safety, especially in unfamiliar or challenging conditions.
Evaluating Manufacturer Quality: Powerful Machinery Anchor Chains
Quality Indicators and Certifications
When you evaluate an anchor chain manufacturer, you should focus on several key quality indicators. Reliable companies maintain strict quality control from raw material selection to the final anchor cable product.
You want to see the whole set of drawings approved by IACS members, which means the anchor cable meets international standards. Manufacturers should offer material fatigue tests and stress analysis on request.
Advanced testing methods, such as magnetic power testing, ultrasonic testing, and fluorescent penetrant inspection, help ensure the anchor cable’s integrity. Load test machines with capacities up to 4000 tons demonstrate a commitment to safety.
You should also look for certifications that prove the anchor cable meets global standards. The table below summarizes important certifications:
Certification Type | Description |
|---|---|
ISO9001 | Quality management system standard |
OSHMS18001 | Occupational health and safety management |
ISO14001 | Environmental management system |
API | American Petroleum Institute standards |
IACS | Type approval by the International Association of Classification Societies members |
Testing methods such as tensile testing, Charpy impact testing, hardness testing, and corrosion testing confirm the anchor cable’s durability and performance. Chemical analysis ensures the anchor cable has the right composition for strength and longevity.
Why Choose Powerful Machinery for Anchor Chains?
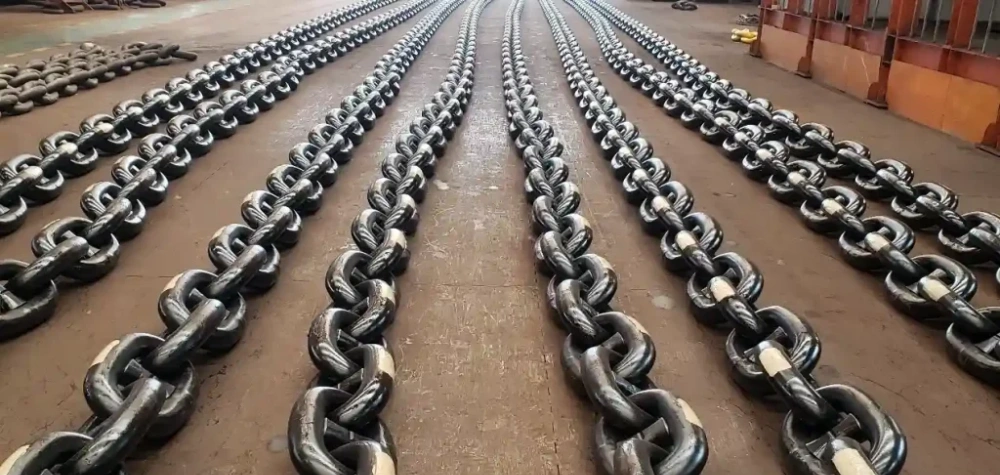

You gain several advantages when you choose Powerful Machinery for your anchor cable needs. The company uses proof-load testing, which means each anchor cable is tested at double the working load limit.
Magnetic particle inspection and ultrasonic testing identify any defects, so you can trust the anchor cable’s reliability. Third-party inspections by organizations like SGS and TÜV add another layer of confidence.
Powerful Machinery anchor chains feature a stud design that prevents tangling and improves weight distribution. Special anti-corrosion treatments keep your anchor cable dependable for decades, even in harsh marine environments.
The anchor cable acts as a shock absorber, reducing stress on your anchor and extending the life of your hardware. High-strength alloy steel construction ensures your anchor cable performs well in tough conditions.
Stud-link chains prevent knotting and guarantee smooth operation through the windlass, adding stability to your anchoring system.
When you select Powerful Machinery, you choose anchor cable products trusted by marine professionals worldwide. You receive certified anchor chains that deliver safety, durability, and peace of mind for every voyage.
Conclusion
You ensure safe and reliable anchoring by following these essential steps:
Choose hot-dip galvanized or stainless steel for your anchor chain.
Select the right grade for strength.
Match the chain size and calibration to your anchor system.
Calculate the correct length for your anchor line.
Inspect for rust, bent links, and worn contact points.
Matching anchor chain material, grade, size, calibration, and anchor line length to your vessel improves stability, safety, and durability. Powerful Machinery provides certified anchor chains that meet strict marine standards. You protect your vessel and anchor line with quality products designed for demanding conditions.
Tip: Regularly inspect your anchor line and anchor chain to prevent failures and maintain performance.
FAQ
What is the best way to inspect my anchor chain for safety?
You should check your anchor chain regularly. Look for rust, bent links, and worn spots. Inspect the line for fraying or damage. Test the anchor and line by pulling hard to confirm holding power. Replace any weak parts to maintain safety.
How do I choose the right anchor chain for maximum holding power?
Select an anchor chain that matches your vessel’s size and weight. Use a high-grade chain for strong holding. Pair the chain with a sturdy anchor and a reliable line. Test the holding power in different conditions to ensure your anchor holds securely.
Can I use rope as part of my anchor line?
You can use a rope with your anchor line. Many boaters combine chain and rope for flexibility. Attach the rope to the anchor chain for better holding. Make sure the rope is marine-grade and strong enough to support the anchor’s holding power.
How much anchor line do I need for secure holding?
Measure the water depth and add the height from the bow to the water. Multiply this by the recommended scope ratio, usually 7:1. This gives you the total anchor line length needed for strong holding power. Always round up for extra safety.
What affects the holding power of my anchor system?
Several factors affect holding power. The anchor type, chain length, and line material all play a role. Seabed conditions and weather also impact holding. Test your anchor line and chain in different environments to confirm reliable holding power.