Wire rope capacity describes the maximum load a wire rope can safely handle during lifting operations. When you understand wire rope capacity, you help prevent accidents caused by common hazards such as corrosion, fatigue, and abrasion.
You also improve workplace safety by recognizing the impact of sling angles, hitch types, and the importance of regular inspection. Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope is engineered for safety and reliability, giving you confidence in every lift. Use this knowledge to create safer lifting conditions for your team and equipment.
Corrosion often results from poor lubrication and is difficult to spot.
Fatigue develops from repeated bending and leads to cracks or failure.
Abrasion happens when the rope contacts sheaves, drums, or other objects, causing significant wear.
Knowing the working load limit and maintaining your wire rope reduces the risk of incidents during safe lifting.
Key Takeaways
Understand wire rope capacity to prevent accidents and improve safety during lifting operations.
Regularly inspect wire ropes for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to ensure safe lifting.
Choose the right wire rope size and type based on load weight and environmental conditions.
Use the working load limit, not the breaking strength, to plan safe lifting operations.
Select appropriate hitch types and maintain optimal sling angles to maximize lifting capacity.
What Is Wire Rope Capacity?
Definition and Key Concepts
Wire rope capacity refers to the maximum load a wire rope can safely support during lifting or rigging operations. You need to understand this value to select the right wire rope for your job. Industry standards, such as ASTM specifications, define how manufacturers classify wire rope.
These standards consider factors like tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue endurance. Most wire ropes use high-grade steel, such as AISI 302/304 or 316 stainless steel, to achieve the required performance.
Wire rope consists of multiple steel wires twisted into strands around a core. This design gives the wire rope both strength and flexibility. The working load limit tells you the maximum force you can safely apply during normal use. The breaking strength shows the highest force the wire rope can withstand before it fails.
You should always use the working load limit, not the breaking strength, when planning lifts.
Key concepts that affect wire rope capacity include:
The D/d ratio, which compares the diameter of the bending surface to the diameter of the wire rope.
A low D/d ratio increases internal friction and can reduce the strength of the wire rope.
Proper rigging practices, such as using padding, help maintain the integrity of the wire rope.
Why Capacity Matters for Safe Lifting?
Wire rope capacity plays a critical role in preventing lifting failures. You must choose wire rope based on its resistance to fatigue and abrasion. Regular inspections help you spot potential problems before they lead to accidents. Proper storage and maintenance also keep your wire rope in top condition.
Wire rope can handle significant tension, but the actual load conditions determine its durability. High cyclic loads can cause rapid fatigue damage, sometimes leading to failure in less than 1,500 cycles. Overloading the wire rope can stretch or break the strands, resulting in catastrophic failure if you exceed the rated capacity.
Always select the appropriate type of wire rope for your application. Regularly inspect and maintain your wire rope to ensure safe lifting operations.
By understanding wire rope capacity, you protect your team, your equipment, and your reputation. You make informed decisions that prevent accidents and extend the life of your wire rope.
Factors Affecting Wire Rope Capacity
Construction and Material

You must consider the construction and material of a wire rope when determining its load capacity. The way manufacturers weave the wires and the type of core used—fiber or steel—directly affect performance.
For example, a steel core increases load capacity and provides better support under heavy loads, while a fiber core offers more flexibility but less strength. The table below compares these core types:
Feature | Fiber Core | Steel Core |
|---|---|---|
Load Capacity | Lower | Higher |
Fatigue Resistance | High | Moderate |
Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope uses high-tensile steel and a non-rotating design. This combination gives you greater safety and stability during lifting. The non-rotating feature keeps the wire rope aligned, reducing the risk of twisting or kinking. You get consistent performance, even in demanding environments.
Diameter and Wire Rope Sizes
The diameter of a wire rope plays a major role in its load capacity. Larger diameters allow you to handle heavier loads. You should always match the wire rope size to the weight of your lift. The chart below shows how wire rope diameter affects rated capacity at different sling angles:
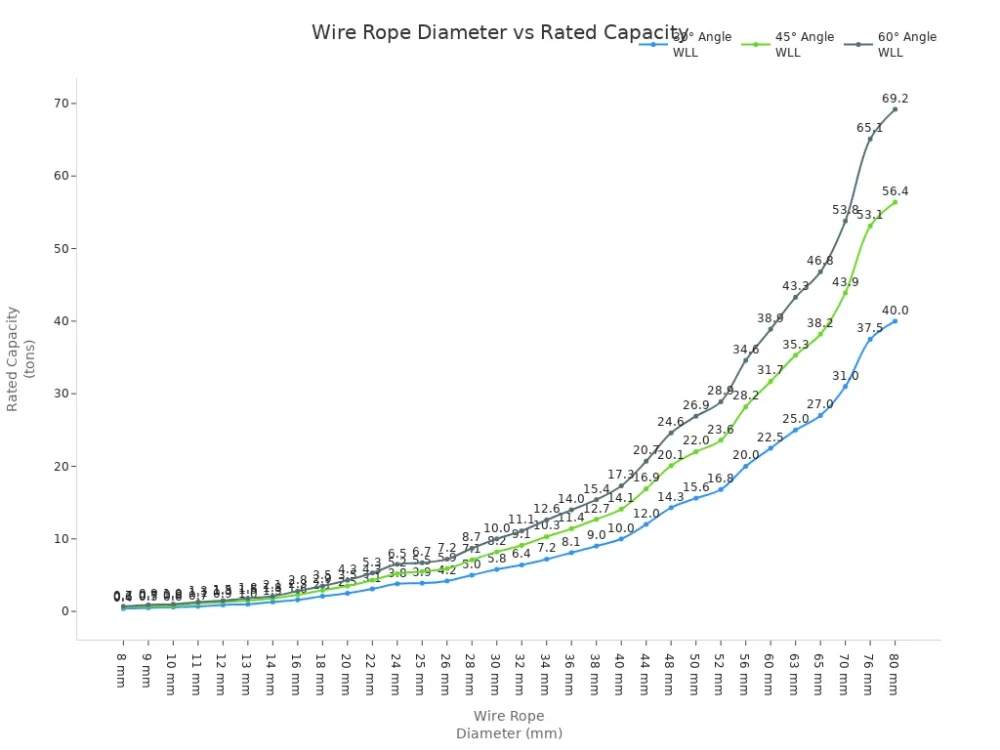
For example, a 10 mm wire rope can handle up to 1.0 tons at a 60° sling angle. If you increase the diameter to 20 mm, the load capacity rises to 4.3 tons at the same angle. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications before making your selection.
Rope Condition and Environment
The condition of your wire rope and the environment where you use it also impact load capacity. Moisture can cause corrosion, which weakens the steel strands. Extreme temperatures and chemical exposure can degrade the material, reducing its strength.
Friction from pulleys or drums may lead to surface damage, pitting, or cracking. You should inspect your wire rope regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or deformation. Lubrication helps reduce friction and preserves the wire rope’s load capacity over time.
Tip: Choose Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope for superior resistance to abrasion and corrosion. Regular maintenance ensures you get the best performance and safety from every lift.
Load Capacity and Working Load Limit
Minimum Breaking Force vs. Safe Load
You must understand the difference between the minimum breaking limit and the safe working load when selecting a wire rope for lifting. The minimum breaking limit tells you the lowest force that will cause the wire rope to fail. Manufacturers determine this value by testing the rope until it breaks.
The safe working load is much lower. It represents the maximum weight you can lift safely without damaging the wire rope.
You should always use the safe working load for planning lifts, not the minimum breaking limit. The working load limit is calculated by dividing the minimum breaking limit by a safety factor. This safety factor protects you from unexpected stresses or flaws in the wire rope.
Here is a quick comparison:
Load limit: The maximum weight a sling can handle without risk of permanent deformation or failure.
Working load capacity: The maximum load recommended for safe use under normal conditions, calculated by dividing the minimum breaking limit by a safety factor.
Working load limit: The maximum safe load a wire rope should carry in actual use, based on the breaking strength and safety factor.
Wire rope grades affect the minimum breaking limit. You can see the typical wire tensile strength grades in the table below:
Rope Grades | Wire tensile strength grades (N/mm²) |
|---|---|
1770 | 1570 – 1960 |
1960 | 1770 – 2160 |
2160 | 1960 – 2160 |
You should always check inspection documents to confirm compliance with rope grade requirements.
Safety Factors in Lifting
You must use a safety factor when calculating the safe working load for any wire rope. The safety factor shows how much force the wire rope can withstand before breaking.
Most lifting applications use a safety factor of 5:1. This means the wire rope can hold five times its safe working load, but you should never approach the minimum breaking limit during actual lifts.
For example, if a wire rope has a safe working load of 10,000 lbs., the safety factor allows for a maximum load of 50,000 lbs. You should always stay within the safe working load to prevent accidents.
Follow these best practices for safe lifting:
Verify all calculations before lifting.
Inspect slings and rigging equipment thoroughly.
Use proper angle measurements and manufacturer charts.
Train personnel on safe rigging practices.
Avoid using over-capacity slings as a substitute for correct calculation.
Maintain documentation of all inspections, lifting plans, and risk assessments.
Adjust rigging to ensure load balance, even with multi-leg lifts.
You protect your team and equipment by respecting working load limits and using the correct safety factor. Always choose a wire rope with a minimum breaking limit that exceeds your lifting needs. Powerful Machinery’s steel wire rope meets strict standards for safe working load and durability, giving you confidence in every lift.
Wire Rope Sling Capacity in Lifting
Types of Hitches and Sling Angles
You must understand how hitch types and sling angles impact wire rope sling capacity. The way you attach a wire rope sling to a load determines how much weight you can lift safely. A vertical hitch lets you use 100% of the sling capacity.
A choker hitch reduces sling capacity to about 75% because the choke angle and bending stress limit performance. A basket hitch can double sling capacity to 200% if you balance the load evenly and keep the legs vertical. If the legs angle outward, the sling capacity drops.
The table below shows how hitch type affects wire rope sling capacity:
Hitch Type | % of Rated Sling Capacity |
|---|---|
Vertical | 100% |
Choker | 75% |
Basket (vertical legs) | 200% |
You should always check the manufacturer’s recommendations and identification tags before lifting. Powerful Machinery’s wire rope sling products meet ASME B30.9 standards. Each sling includes a tag with rated load, diameter, and number of legs for your safety.
How Sling Capacity Changes with Angle?
Sling capacity changes as you adjust the angle between the legs of a wire rope sling and the horizontal. When you lift with a wide sling angle, tension increases on each leg.
The closer the angle gets to horizontal, the higher the tension and the lower the sling capacity. Angles below 30 degrees are not recommended because they create dangerous tension levels.
The optimal sling angle is close to 90 degrees.
As the angle decreases, sling capacity drops sharply.
You can calculate tension using: Tension = Load / (number of legs × sin(angle)).
Charts from ASME and WSTDA show how sling capacity reduces at different angles. For example, at a 60° angle, sling capacity is about 87% of the rated value. At 30°, it drops to 50%. Always use these reduction factors to choose the right wire rope sling for your lift.
Tip: Select Powerful Machinery’s certified wire rope sling for reliable performance. You get clear identification, robust construction, and full compliance with international safety standards.
Wire Rope Capacity Calculation Guide
Step-by-Step Calculation
You must follow a systematic approach to calculate wire rope capacity for safe lifting. This process ensures you select the right equipment and avoid overloading. Use these steps each time you plan a lift:
Determine the Load Weight and Center of Gravity
Identify the total weight of the load. Locate the center of gravity to ensure balanced lifting.Select the Hitch Type and Initial Sling Configuration
Decide if you will use a vertical, choker, or basket hitch. The hitch type directly affects lifting capacity.Calculate the Sling Angle (α)
Measure the angle between the sling legs and the horizontal. The sling angle impacts the tension on each leg.Calculate the True Tension on Each Leg
Use the formula:Tension = Load / (number of legs × sin(angle))
This calculation helps you understand the actual force on each sling leg.Select a Sling and Check Its Capacity
Refer to the lifting load chart to match the sling diameter and configuration to your load. The chart below shows how the diameter affects the safe working load:Diameter (inches)
Safe Working Load (SWL) (tons)
0.5
2
1
8
Always use the lifting load chart provided by the manufacturer for accurate values.
Assess the D/d Ratio
Compare the diameter of the sheave or drum (D) to the diameter of the wire rope (d). A low D/d ratio can reduce wire rope strength.Calculate the Effective Capacity of the Selected Sling
Adjust the rated capacity based on the sling angle and hitch type. Use the lifting load chart to confirm the final value.Final Verdict
Ensure the selected wire rope and sling configuration meet or exceed the required lifting capacity. Double-check all calculations before proceeding.
Tip: Always consider dynamic loading when calculating wire rope capacity. Sudden movements or shocks can increase the force on the rope beyond static values.
You can apply this method to a wide range of wire rope applications, from construction to marine lifting. Following these steps helps you maximize safety and efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
You must avoid common errors when assessing wire rope capacity. These mistakes can lead to dangerous situations and equipment failure:
Misinterpretation of the hitch type
Choosing the wrong hitch reduces lifting capacity and increases risk.Neglecting the sling angle
Ignoring the sling angle leads to underestimating the true tension on each leg.Incorrect D/d ratio
Using a sheave or drum with a small diameter weakens the wire rope and reduces lifting capacity.
Other frequent mistakes include:
Overlooking the effects of dynamic loading, which can cause unexpected spikes in tension.
Failing to consult the lifting load chart for the correct wire rope size and configuration.
Using wire rope beyond its rated capacity in demanding wire rope applications.
Note: Regular training and review of lifting procedures help you avoid these pitfalls. Always use certified products like Powerful Machinery’s steel wire rope for reliable performance.
By following a structured calculation process and avoiding these mistakes, you ensure safe and effective lifting operations every time.
Choosing the Right Steel Wire Rope

Matching Rope Size to Load Capacity
You must match the wire rope size to your load requirements to ensure safe and efficient lifting. Start by considering the weight of your load and the type of lifting equipment you plan to use. The diameter of the wire rope directly affects its capacity for heavy lifting.
Larger diameters support greater loads, while smaller diameters suit lighter tasks. Construction also matters. The number and arrangement of wire strands influence sling strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance.
When selecting a wire rope, review the core type. A steel core increases strength and durability, while a fiber core offers more flexibility. Both options serve different lifting needs. The sling angle plays a critical role in determining the actual load each leg of the sling will carry.
As the sling angle decreases, tension on each leg increases, reducing overall sling strength. Always calculate the sling angle before lifting.
Environmental conditions also impact your choice. Use the table below to assess how your work environment affects wire rope performance:
Environmental Factor | Impact on Steel Wire Rope |
|---|---|
Marine/Coastal Areas | Salt exposure accelerates corrosion. |
Industrial Zones | Chemicals or acids can weaken the wire surface. |
UV and Temperature | High temperatures may lower tensile capacity. |
Choose a wire rope grade that matches your lifting demands:
Wire Rope Grade | Minimum Tensile Strength |
|---|---|
1770 | 1770 N/mm² |
1960 | 1960 N/mm² |
2160 | 2160 N/mm² |
Selecting Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope
Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope stands out for demanding heavy lifting applications. You benefit from high tensile strength, which allows the rope to handle significant loads without risk of failure.
The non-rotating design and multi-layer construction enhance fatigue resistance, letting you perform repeated lifts with confidence. This design also helps maintain stability, especially when the sling angle changes during complex lifts.
Key features include:
High breaking strength for maximum safety.
Excellent fatigue resistance for long service life.
Superior resistance to corrosion and abrasion, even in harsh environments.
Consistent performance with a variety of lifting equipment.
You extend the lifespan of your lifting equipment by choosing a wire rope with these qualities. Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope meets international standards, making it a reliable choice for any project where safety and performance matter most.
Tip: Always select a wire rope that exceeds your minimum load requirements and matches your expected sling angle. This approach ensures safe, efficient, and trouble-free heavy lifting operations.
Safe Lifting Checklist and Maintenance
Pre-Lift Inspection Steps
You must inspect your wire rope before every lift to ensure safety. Start with a thorough visual check. Look for cuts, frays, or broken wires along the entire length of the rope. Clean off any dirt or grime so you can see all parts clearly. Examine the identification tag to confirm the load capacity and usage limitations.
If the tag is missing or unreadable, do not use the rope.
Check for kinks, birdcaging, or crushing. These signs indicate that the wire rope has suffered damage and should not be used. Inspect the end fittings and hardware for cracks or deformation. Remove any damaged rigging hardware from service immediately. Always verify that you are using the correct sling type for your lift.
Tip: If you find any damage during inspection, remove the wire rope from service and destroy it to prevent accidental use.
You should also measure the diameter of the rope at several points. This helps you detect internal wear or stretching. Assess the lay length and look for signs of corrosion, especially in areas that experience the most stress. Keep detailed records of inspection dates, findings, and any repairs.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper maintenance extends the life of your steel wire rope and ensures reliable performance. Store your wire ropes in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid exposure to chemicals or moisture that can cause corrosion. Cover the ropes to protect them from dust and environmental damage.
Install wire ropes correctly by applying uniform tension and avoiding twists. Clean the rope before applying lubricant. Use a penetrating lubricant to reach the inner wires and reduce friction. Schedule regular inspections to monitor for broken wires, corrosion, or wear. Pay special attention to the most frequently stressed zones.
Regular cleaning, lubrication, and proper storage help you maximize the lifespan of your wire rope. Consistent maintenance reduces the risk of unexpected failures and keeps your lifting operations safe.
Conclusion
You protect your team and equipment when you calculate wire rope capacity accurately for lifting operations. This process ensures you respect weight limits and avoid dangerous overloads. Certified products like Powerful Machinery’s Steel Wire Rope give you confidence in every lift.
Always perform daily visual inspections and schedule thorough checks by a competent person.
Look for wire breaks, corrosion, and diameter changes before each use.
For safe lifting solutions, consult with industry experts. Review manufacturer profiles, compare capabilities, and request certifications to guarantee quality and safety.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of a non-rotating steel wire rope?
You gain increased safety and stability during lifting. The non-rotating design prevents twisting and kinking, which helps you maintain control and reduces the risk of accidents in critical operations.
How do you determine the correct wire rope specifications for your project?
You should review the load weight, sling angle, and environmental conditions. Always consult manufacturer charts and guidelines to match the wire rope specifications to your lifting requirements.
How often should you inspect your steel wire rope?
You need to inspect your steel wire rope before every use. Schedule detailed inspections at regular intervals based on usage frequency and operating environment. Early detection of damage helps you prevent failures.
Can you use steel wire rope outdoors?
You can use steel wire rope outdoors. Choose a product with high resistance to corrosion and abrasion. Powerful Machinery’s steel wire rope performs well in harsh environments, including marine and construction sites.
What should you do if you find broken wires during inspection?
You must remove the wire rope from service immediately. Do not attempt repairs. Replace the damaged rope to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards.


