Comparing Strength, Durability, and Applications
Explore the key differences between Grade 43 and Grade 70 chains.
Features | Grade 43 High Test Chain | Grade 70 Transport Chain |
|---|---|---|
Material Composition | Carbon steel for general use. | Heat-treated carbon steel for strength. |
Strength Rating | Lower strength than Grade 70. | Approximately 20% stronger than Grade 43. |
Working Load Limit | Suitable for moderate loads. | Higher limits for heavy-duty tasks. |
Common Applications | Used in towing and logging. | Ideal for transport and load securement. |
Finish Options | Various finishes available. | Typically features a yellow zinc finish. |
Safety Standards | Meets ASTM and NACM standards. | Meets ASTM, NACM, and DOT standards. |
Durability | Durable for general tasks. | More durable due to heat treatment. |
Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher cost due to enhanced features. |
When you compare grade 43 vs grade 70 chain, you notice key differences in strength and working load limits. Grade 43 chain handles general-purpose tasks like towing and cargo securing.
Grade 70 chain offers higher strength for heavy-duty applications, including transport and load binding. Take a look at the table below to see how each chain performs:
Chain Grade | Minimum Tensile Strength | Working Load Limit (WLL) | Safety Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
Grade 43 | 11,600 pounds | 3:1 | 3:1 |
Grade 70 | 7,600 pounds | 4:1 | 4:1 |
You should choose grade 70 chain when you need maximum durability and safety for demanding jobs.
Key Takeaways
Grade 70 chains are about 20% stronger than Grade 43 chains, making them ideal for heavy-duty transport and load securement.
Always check the working load limit (WLL) before using a chain. Grade 70 provides a safety margin for larger or more valuable loads.
Choose Grade 43 for general-purpose tasks like towing and cargo securing. Opt for Grade 70 when you need maximum durability and safety.
Inspect chains regularly for wear and ensure they meet safety standards. Look for stamped markings to verify the chain grade.
Consider environmental conditions when selecting a chain. Grade 70 often has a protective finish that resists corrosion and improves visibility.
Chain Grades Overview

Chain grades help you identify the strength and suitability of a chain for specific tasks. You need to understand these grades before choosing the right chain for your job. Chain grades are defined by their ultimate breaking strength per square millimeter.
The most common grades include G30, G43, G70, G80, G100, and Grade 120. Each grade serves a different purpose, ranging from general utility to extremely heavy-duty applications.
G30: Standard grade for general use.
G43: Higher strength than G30, suitable for more demanding applications.
G70: Used in transport and heavy lifting.
G80: Common in rigging and lifting.
G100: Superior overhead lifting and rigging.
Grade 120: Designed for extreme loads.
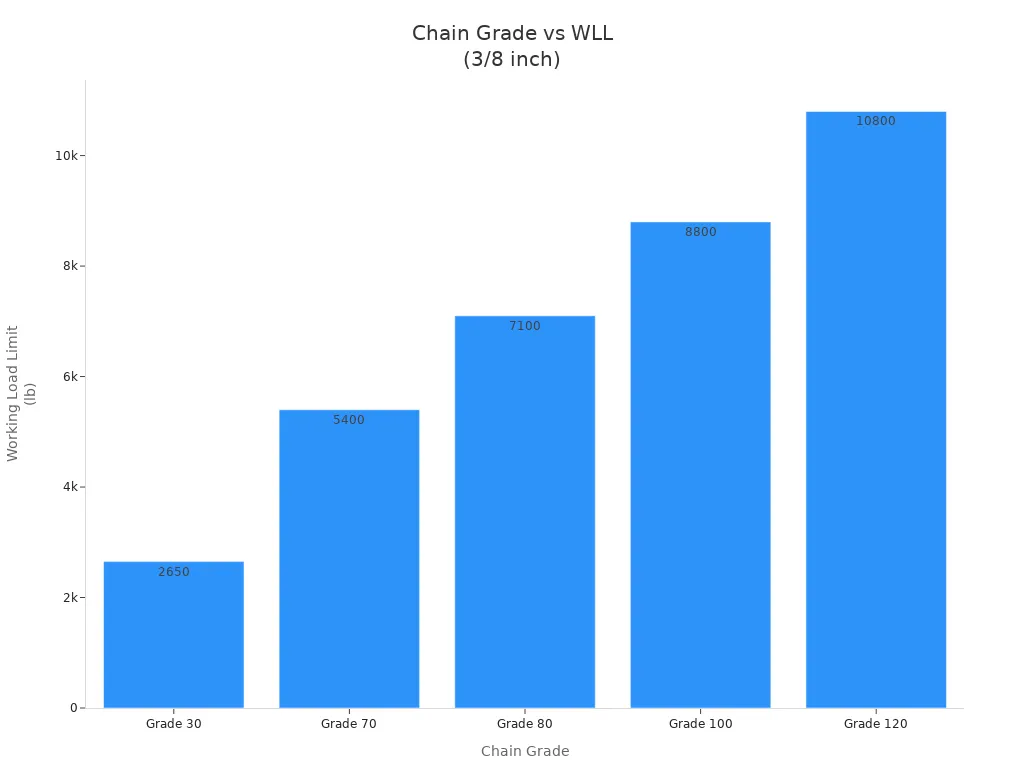
The table below shows how chain grades impact your selection process:
Chain Grade | Material | Primary Use | WLL Example (3/8″) | Overhead Lifting Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Grade 30 | Low-carbon steel | General utility, lashing | 2,650 lb | NOT for overhead lifting |
Grade 43 | Carbon steel | Towing, cargo securement | 4,200 lb | NOT for overhead lifting |
Grade 70 | Heat-treated carbon steel | Transport, cargo securement | 5,400 lb | NOT for overhead lifting |
Grade 80 | Alloy steel | Overhead lifting, towing | 7,100 lb | YES |
Grade 100 | Alloy steel | Superior lifting, rigging | 8,800 lb | YES |
Grade 120 | Alloy steel | Extreme applications | 10,800 lb | YES |
Grade 43 Chain
You can rely on Powerful Machinery’s G43 High Test Chain for demanding tasks. This chain grade uses carbon steel, which provides durability and strength for towing, logging, and cargo securing. The G43 chain meets ASTM and NACM standards, ensuring safety and reliability.
You can choose from several finishes, including self-colored, bright, zinc-plated, or galvanized, to match your environment. The manufacturing process involves forming and welding carbon steel, which gives the chain its robust structure.
Specification | Details |
|---|---|
Grade | 43 |
Finish | Self Colored, Bright, Zinc Plated, Galvanized |
Material | Carbon Steel |
Standards | Meets ASTM & NACM standards |
Grade 70 Chain
Powerful Machinery’s G70 Transport Chain offers even greater strength. This chain grade uses heat-treated carbon steel, which undergoes quenching and tempering. These steps transform the steel into a hard, tough material that resists impacts and fatigue.
The G70 chain is ideal for transport, load binding, and heavy-duty cargo control. You benefit from a yellow zinc finish that protects against corrosion. The chain complies with NACM96 standards and comes with proof testing and test certificates available on request.
Compliance Certification | Description |
|---|---|
NACM96 | Complies with the requirements of NACM96 |
Proof Testing | Chains are proof tested |
Test Certificates | Available on request |
Tip: Always check the chain grade and certification before using a chain for critical applications. This ensures you meet safety standards and get the right performance for your needs.
Grade 43 vs Grade 70 Chain Comparison

Strength and Load Limits
When you compare grade 43 vs grade 70 chain, you see a clear difference in strength. Grade 70 chains are about 20% stronger than grade 43 chains. This increase in strength comes from the heat-treated carbon steel used in grade 70.
You can rely on grade 70 for heavy-duty jobs that require higher working load limits and breaking force.
Grade 43 chains handle general towing, cargo securing, and logging.
Grade 70 chains support trucking, trailer tie-downs, and heavy load securement.
Grade 70 chains offer higher working load limits, making them suitable for demanding applications.
You should always check the working load limit before using any chain. Grade 70 gives you an extra safety margin for larger or more valuable loads.
Material and Durability
The material and finish of a chain affect its durability and resistance to wear. Grade 43 chains use carbon steel, which provides solid strength for most jobs. Grade 70 chains use heat-treated carbon steel, which increases both strength and toughness.
Grade 70 chains often feature a gold chromate or yellow zinc finish.
This finish improves visibility and adds corrosion resistance.
Even with protective finishes, chains may still corrode in harsh environments.
Grade 43 chains come in finishes like self-colored, bright, zinc-plated, or galvanized. These finishes help protect against rust and extend the life of the chain. You should choose the finish that matches your work environment for the best results.
Note: A gold chromate finish on grade 70 chains makes them easy to identify and helps prevent corrosion, but you should still inspect chains regularly for signs of wear.
Common Uses
You need to match the chain grade to your specific application. Grade 43 and grade 70 chains serve different industries and tasks. The table below highlights common uses for grade 43 chains:
Industry/Application | Description |
|---|---|
Trucking | Used as a tow and binder chain. |
Agriculture | Commonly utilized for tie down applications. |
Construction | Suitable for various heavy-duty applications. |
Grade 70 chains see frequent use in:
Trucking and transportation for securing cargo.
Trailer tie-downs and load binding.
Towing and recovery operations.
Logging and forestry work.
When you need a chain for general-purpose tasks, grade 43 is a reliable choice. For heavy-duty transport, cargo control, or when regulations require higher strength, grade 70 is the better option.
Safety Standards
Regulations
When you select between grade 43 and grade 70 chains, you must consider the regulations that govern their use. Different chain grades must meet specific standards to ensure safety and reliability.
The most important standards come from ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), NACM (National Association of Chain Manufacturers), and DOT (Department of Transportation). These organizations set the rules for manufacturing, testing, and using chains in various industries.
Here is a comparison of regulatory compliance for each chain grade:
Chain Grade | Compliance with ASTM | Compliance with NACM | Compliance with DOT |
|---|---|---|---|
Grade 43 | Yes | Yes | N/A |
Grade 70 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
You see that both grade 43 and grade 70 chains meet ASTM and NACM standards. However, only grade 70 chain meets DOT requirements, which makes it the preferred choice for transport and cargo control on public roads.
Compliance
You must always use compliant chain grades to protect yourself and your business. Using a non-compliant chain can lead to serious legal and financial consequences. Here are some possible outcomes if you ignore regulations:
Monetary fines that can impact your bottom line.
Civil penalties that compensate for harm or deter future violations.
Criminal penalties, including possible imprisonment for severe cases.
Administrative sanctions, such as license suspension or revocation.
Injunctions that require you to stop certain activities.
Seizure of assets by authorities.
Loss of privileges, like exclusion from government contracts.
Damage to your reputation and loss of customer trust.
Mandatory corrective actions to address violations.
Exclusion from regulatory programs or trade associations.
You should also check for proper markings on every chain. ASTM standards require each grade to have a stamped code for identification. You will find markings like “G43” or “G70” on the chain links.
Chains also display the working load limit (WLL) and a batch code for quality tracking. These markings help you verify that the chain meets the required standards and is safe for your application.
Grade | Markings | Description |
|---|---|---|
G43 | Stamped code | Suitable for moderate loads |
G70 | Stamped code | Designed for heavy-duty use |
WLL | Working Load Limit | Shows the maximum safe load |
Batch Code | Heat code | Tracks the manufacturing batch |
Tip: Always inspect the markings before using a chain. This simple step helps you avoid costly mistakes and ensures you follow all safety standards.
Grade 43 Chain vs Grade 70: How to Choose
Application Scenarios
You need to match the right chain to your job. Start by considering the load you plan to secure or move. Grade 43 works well for general towing, logging, and basic cargo securing.
Grade 70 offers about 20% more strength, making it the better choice for heavy-duty transport, load securement, and trucking. Neither chain grade is approved for overhead lifting, so you should never use them for that purpose.
Chain Grade | Load Rating Comparison | Material Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Grade 43 | Lower (Base) | Standard steel, not heat-treated | Towing, logging, general use |
Grade 70 | Approximately 20% higher | Heat-treated carbon steel, gold chromate | Load securement, trucking, logging |
Environmental conditions also play a role. If you work in harsh weather or corrosive environments, choose a chain with a protective finish. Grade 70 chains often come with a gold chromate finish, which helps resist corrosion and increases visibility.
Tip: Always check the chain markings and working load limit before use. This ensures you select the right chain for your application.
Decision Factors
When you decide between grade 43 and grade 70, focus on these factors:
Load Requirements: Grade 70 supports heavier loads. Upgrade from grade 43 to grade 70 when your job demands higher strength or when regulations require it.
Material and Durability: Grade 70 chains use heat-treated carbon steel, which provides greater durability for demanding tasks.
Cost Considerations: Grade 43 chains usually cost less, making them suitable for general use. Grade 70 chains cost more but offer higher strength and better finishes for tough jobs.
Chain Grade | Material | Applications | Finish |
|---|---|---|---|
Grade 43 | Carbon Steel | Trucking, Agriculture, Construction | N/A |
Grade 70 | Heat-Treated Carbon Steel | Load Securement, Tie Down, Trucking | Gold Chromate Finish |
You also benefit from Powerful Machinery’s flexible payment options, such as a 30-day credit account. Fast delivery ensures you get the chain you need without delay, keeping your operations running smoothly.
Note: Always consider safety standards and compliance before making your final choice. The right chain grade protects your equipment, your team, and your business.
Conclusion
When you compare grade 43 vs grade 70 chain, you see clear differences in strength, material, and best use. Review the table below for a quick summary:
Feature | Grade 43 | Grade 70 |
|---|---|---|
Material Composition | Heat-treated steel | Higher strength, heat-treated carbon steel |
Load Rating | Lower than Grade 70 | Approximately 20% higher than Grade 43 |
Typical Applications | General purpose, towing, farming | Load securement, towing, used by truckers and loggers |
Before you choose, always check safety standards and working load limits. Follow these tips:
Inspect your chain regularly for wear or damage.
Consult manufacturer guidelines and safety regulations.
Select the right chain for your specific job.
Prioritize safety and proper chain selection to protect your equipment and team.
FAQ
What is the main difference between Grade 43 and Grade 70 chains?
Grade 70 chains have higher strength and working load limits than Grade 43 chains. You should use Grade 70 for heavy-duty transport and load securement. Grade 43 works best for general towing and cargo tasks.
Can you use Grade 43 and Grade 70 chains for overhead lifting?
No, you cannot use either chain for overhead lifting. Neither grade is rated for lifting people or loads above ground. For lifting, you need Grade 80 or higher.
How do you identify Grade 43 vs Grade 70 chains?
You can check the stamped markings on each chain link. Grade 43 chains show “G43,” and Grade 70 chains show “G70.” Grade 70 chains often have a gold chromate finish for easy identification.
Which chain grade should you choose for DOT-regulated transport?
You should choose Grade 70 chains for DOT-regulated transport. Grade 70 meets Department of Transportation requirements for securing cargo on public roads. Grade 43 does not meet these regulations.
Are Grade 70 chains more resistant to corrosion than Grade 43?
Grade 70 chains often have a yellow zinc or gold chromate finish, which provides better corrosion resistance. Grade 43 chains may have zinc-plated or galvanized finishes, but Grade 70’s finish offers higher visibility and protection.
